Formation of deoxyguanosine cross-links from calf thymus DNA treated with acrolein and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal
- PMID: 20964440
- PMCID: PMC2990652
- DOI: 10.1021/tx100179g
Formation of deoxyguanosine cross-links from calf thymus DNA treated with acrolein and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal
Abstract
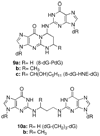
Acrolein (AC) and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) are endogenous bis-electrophiles that arise from the oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids. AC is also found in high concentrations in cigarette smoke and automobile exhaust. These reactive α,β-unsaturated aldehyde (enal) covalently modify nucleic acids, to form exocyclic adducts, where the three-carbon hydroxypropano unit bridges the N1 and N(2) positions of deoxyguanosine (dG). The bifunctional nature of these enals allows them to undergo reaction with a second nucleophilic group and form DNA cross-links. These cross-linked enal adducts are likely to contribute to the genotoxic effects of both AC and HNE. We have developed a sensitive mass spectrometric method to detect cross-linked adducts of these enals in calf thymus DNA (CT DNA) treated with AC or HNE. The AC and HNE cross-linked adducts were measured by the stable isotope dilution method, employing a linear quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometer and consecutive reaction monitoring at the MS(3) or MS(4) scan stage. The lower limit of quantification of the cross-linked adducts is ∼1 adduct per 10(8) DNA bases, when 50 μg of DNA is assayed. The cross-linked adducts occur at levels that are ∼1-2% of the levels of the monomeric 1,N(2)-dG adducts in CT DNA treated with either enal.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Chemistry and biology of DNA containing 1,N(2)-deoxyguanosine adducts of the alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes acrolein, crotonaldehyde, and 4-hydroxynonenal.Chem Res Toxicol. 2009 May;22(5):759-78. doi: 10.1021/tx9000489. Chem Res Toxicol. 2009. PMID: 19397281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a method for quantification of acrolein-deoxyguanosine adducts in DNA using isotope dilution-capillary LC/MS/MS and its application to human brain tissue.Anal Chem. 2005 Sep 15;77(18):5982-9. doi: 10.1021/ac050624t. Anal Chem. 2005. PMID: 16159131
-
Rearrangement of the (6S,8R,11S) and (6R,8S,11R) exocyclic 1,N2-deoxyguanosine adducts of trans-4-hydroxynonenal to N2-deoxyguanosine cyclic hemiacetal adducts when placed complementary to cytosine in duplex DNA.J Am Chem Soc. 2008 Aug 20;130(33):10898-906. doi: 10.1021/ja801824b. Epub 2008 Jul 29. J Am Chem Soc. 2008. PMID: 18661996 Free PMC article.
-
Repair kinetics of acrolein- and (E)-4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-derived DNA adducts in human colon cell extracts.Mutat Res. 2013 Nov-Dec;751-752:15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2013.09.004. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Mutat Res. 2013. PMID: 24113140 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of trans-4-hydroxy-2-nonenal- and other enal-derived cyclic DNA adducts from omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids and their roles in DNA repair and human p53 gene mutation.Mutat Res. 2003 Oct 29;531(1-2):25-36. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2003.07.001. Mutat Res. 2003. PMID: 14637245 Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-adductomics: Advancing mass spectrometry techniques for comprehensive exposome characterization.Trends Analyt Chem. 2024 Nov;180:117900. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2024.117900. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Trends Analyt Chem. 2024. PMID: 39246549
-
Looking beneath the surface to determine what makes DNA damage deleterious.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2014 Aug;21:48-55. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2014.03.018. Epub 2014 Apr 22. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 24762292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Approaches for Biomonitoring Exposure to the Human Carcinogen Aristolochic Acid.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2015 Jul 1;4(4):763-776. doi: 10.1039/C5TX00052A. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2015. PMID: 26366284 Free PMC article.
-
Probing DNA interstrand cross-link formation by an oxidized abasic site using nonnative nucleotides.Bioorg Med Chem. 2011 Oct 1;19(19):5788-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2011.08.024. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Bioorg Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21903404 Free PMC article.
-
Simple, High-Yield Syntheses of DNA Duplexes Containing Interstrand DNA-DNA Cross-Links Between an N(4) -Aminocytidine Residue and an Abasic Site.Curr Protoc Nucleic Acid Chem. 2016 Jun 1;65:5.16.1-5.16.15. doi: 10.1002/cpnc.3. Curr Protoc Nucleic Acid Chem. 2016. PMID: 27248783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Esterbauer H, Schaur RJ, Zollner H. Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1991;11:81–128. - PubMed
-
- Esterbauer H. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of lipid-oxidation products. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1993;57 779S–785S. - PubMed
-
- Niki E. Lipid peroxidation: Physiological levels and dual biological effects. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009;47:469–484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

