Basolateral potassium (IKCa) channel inhibition prevents increased colonic permeability induced by chemical hypoxia
- PMID: 20966032
- PMCID: PMC3025504
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00472.2009
Basolateral potassium (IKCa) channel inhibition prevents increased colonic permeability induced by chemical hypoxia
Abstract
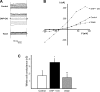
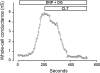
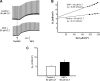
Major liver resection is associated with impaired intestinal perfusion and intestinal ischemia, resulting in decreased mucosal integrity, increased bacterial translocation, and an increased risk of postoperative sepsis. However, the mechanism by which ischemia impairs intestinal mucosal integrity is unclear. We therefore evaluated the role of Ca(2+)-sensitive, intermediate-conductance (IK(Ca)) basolateral potassium channels in enhanced intestinal permeability secondary to chemical hypoxia. The effects of chemical hypoxia induced by 100 μM dinitrophenol (DNP) and 5 mM deoxyglucose (DG) on basolateral IK(Ca) channel activity and whole cell conductance in intact human colonic crypts, and paracellular permeability (G(S)) in isolated colonic sheets, were determined by patch-clamp recording and transepithelial electrical measurements, respectively. DNP and DG rapidly stimulated IK(Ca) channels in cell-attached basolateral membrane patches and elicited a twofold increase (P = 0.004) in whole cell conductance in amphotericin B-permeabilized membrane patches, changes that were inhibited by the specific IK(Ca) channel blockers TRAM-34 (100 nM) and clotrimazole (CLT; 10 μM). In colonic sheets apically permeabilized with nystatin, DNP elicited a twofold increase (P = 0.005) in G(S), which was largely inhibited by the serosal addition of 50 μM CLT. We conclude that, in intestinal epithelia, chemical hypoxia increases G(S) through a mechanism involving basolateral IK(Ca) channel activation. Basolateral IK(Ca) channel inhibition may prevent or limit increased intestinal permeability during liver surgery.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Somatostatin peptides prevent increased human colonic epithelial permeability induced by hypoxia.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024 Nov 1;327(5):G701-G710. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00057.2024. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39226584
-
Identification and functional characterization of the intermediate-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channel (IK-1) in biliary epithelium.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009 Nov;297(5):G1009-18. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00223.2009. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009. PMID: 20501432 Free PMC article.
-
Active K+ secretion through multiple KCa-type channels and regulation by IKCa channels in rat proximal colon.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003 Jul;285(1):G185-96. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00337.2002. Epub 2003 Feb 26. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12606302
-
The Ca2+-activated K+ channel of intermediate conductance: a molecular target for novel treatments?Curr Drug Targets. 2001 Dec;2(4):401-22. doi: 10.2174/1389450013348173. Curr Drug Targets. 2001. PMID: 11732639 Review.
-
The Ca2+-activated K+ channel of intermediate conductance:a possible target for immune suppression.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2002 Dec;6(6):623-36. doi: 10.1517/14728222.6.6.623. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2002. PMID: 12472376 Review.
Cited by
-
Priming approaches to improve the efficacy of mesenchymal stromal cell-based therapies.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 May 2;10(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1224-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31046833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Effects on Ion Transport across Rat Colonic Epithelium.Front Physiol. 2016 Jun 21;7:247. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00247. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27445839 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and molecular identification of a TASK-1 potassium channel regulating chloride secretion through CFTR channels in the shark rectal gland: implications for cystic fibrosis.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016 Dec 1;311(6):C884-C894. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00030.2016. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27653983 Free PMC article.
-
Somatostatin peptides prevent increased human colonic epithelial permeability induced by hypoxia.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024 Nov 1;327(5):G701-G710. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00057.2024. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39226584
-
Potassium channels in intestinal epithelial cells and their pharmacological modulation: a systematic review.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021 Apr 1;320(4):C520-C546. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00393.2020. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33326312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blumenstein I, Gerhard R, Ries J, Kottra G, Stein J. Regulation of mastoparan-induced increase of paracellular permeability in T84 cells by RhoA and basolateral potassium channels. Biochem Pharmacol 65: 1151–1161, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Brancatisano R, Isla A, Habib N. Is radical hepatic surgery safe? Am J Surg 175, 161–163, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Brugnara C, Armsby CC, Sakamoto M, Rifai N, Alper SL, Platt O. Oral administration of clotrimazole and blockade of human erythrocyte Ca2+-activated K+ channel: the imidazole ring is not required for inhibitory activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 273: 266–272, 1995 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

