Intrarenal renin angiotensin system revisited: role of megalin-dependent endocytosis along the proximal nephron
- PMID: 20966072
- PMCID: PMC3009920
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.150284
Intrarenal renin angiotensin system revisited: role of megalin-dependent endocytosis along the proximal nephron
Abstract
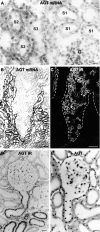
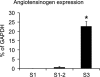
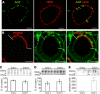
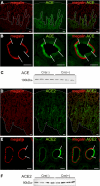
The existence of a local renin angiotensin system (RAS) of the kidney has been established. Angiotensinogen (AGT), renin, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), angiotensin receptors, and high concentrations of luminal angiotensin II have been found in the proximal tubule. Although functional data have documented the relevance of a local RAS, the dualism between biosynthesis and endocytotic uptake of its components and their cellular processing has been incompletely understood. To resolve this, we have selectively analyzed their distribution, endocytosis, transcytosis, and biosynthesis in the proximal tubule. The presence of immunoreactive AGT, restricted to the early proximal tubule, was due to its retrieval from the ultrafiltrate and storage in endosomal and lysosomal compartments. Cellular uptake was demonstrated by autoradiography of radiolabeled AGT and depended on intact endocytosis. AGT was identified as a ligand of the multiple ligand-binding repeats of megalin. AGT biosynthesis was restricted to the proximal straight tubule, revealing substantial AGT mRNA expression. Transgenic AGT overexpression under the control of an endogenous promoter was also restricted to the late proximal tubule. Proximal handling of renin largely followed the patterns of AGT, whereas its local biosynthesis was not significant. Transcytotic transport of AGT in a proximal cell line revealed a 5% recovery rate after 1 h. ACE was expressed along late proximal brush-border membrane, whereas ACE2 was present along the entire segment. Surface expression of ACE and ACE2 differed as a function of endocytosis. Our data on the localization and cellular processing of RAS components provide new aspects of the functional concept of a "self-contained" renal RAS.
Figures




References
-
- Quan A., Baum M. (2000) Nephron 84, 103–110 - PubMed
-
- Kobori H., Nangaku M., Navar L. G., Nishiyama A. (2007) Pharmacol. Rev. 59, 251–287 - PubMed
-
- Braam B., Mitchell K. D., Fox J., Navar L. G. (1993) Am. J. Physiol. 264, F891–F898 - PubMed
-
- Le T. H., Coffman T. M. (2008) Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 17, 57–63 - PubMed
-
- Guyton A. C. (1991) Science 252, 1813–1816 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

