The interplay between tissue plasminogen activator domains and fibrin structures in the regulation of fibrinolysis: kinetic and microscopic studies
- PMID: 20966169
- PMCID: PMC3031486
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-290338
The interplay between tissue plasminogen activator domains and fibrin structures in the regulation of fibrinolysis: kinetic and microscopic studies
Abstract
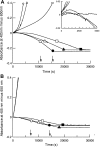
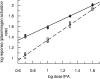
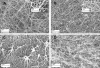
Regulation of tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) depends on fibrin binding and fibrin structure. tPA structure/function relationships were investigated in fibrin formed by high or low thrombin concentrations to produce a fine mesh and small pores, or thick fibers and coarse structure, respectively. Kinetics studies were performed to investigate plasminogen activation and fibrinolysis in the 2 types of fibrin, using wild-type tPA (F-G-K1-K2-P, F and K2 binding), K1K1-tPA (F-G-K1-K1-P, F binding), and delF-tPA (G-K1-K2-P, K2 binding). There was a trend of enzyme potency of tPA > K1K1-tPA > delF-tPA, highlighting the importance of the finger domain in regulating activity, but the differences were less apparent in fine fibrin. Fine fibrin was a better surface for plasminogen activation but more resistant to lysis. Scanning electron and confocal microscopy using orange fluorescent fibrin with green fluorescent protein-labeled tPA variants showed that tPA was strongly associated with agglomerates in coarse but not in fine fibrin. In later lytic stages, delF-tPA-green fluorescent protein diffused more rapidly through fibrin in contrast to full-length tPA, highlighting the importance of finger domain-agglomerate interactions. Thus, the regulation of fibrinolysis depends on the starting nature of fibrin fibers and complex dynamic interaction between tPA and fibrin structures that vary over time.
Figures



References
-
- Weisel JW, Litvinov RI. The biochemical and physical process of fibrinolysis and effects of clot structure and stability on the lysis rate. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2008;6(3):161–180. - PubMed
-
- Carr ME, Jr, Alving BM. Effect of fibrin structure on plasmin-mediated dissolution of plasma clots. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1995;6(6):567–573. - PubMed
-
- Gabriel DA, Muga K, Boothroyd EM. The effect of fibrin structure on fibrinolysis. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(34):24259–24263. - PubMed
-
- Collet JP, Park D, Lesty C, et al. Influence of fibrin network conformation and fibrin fiber diameter on fibrinolysis speed: dynamic and structural approaches by confocal microscopy. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20(5):1354–1361. - PubMed
-
- Kolev K, Tenekedjiev K, Komorowicz E, Machovich R. Functional evaluation of the structural features of proteases and their substrate in fibrin surface degradation. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(21):13666–13675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

