Mechanisms of proton conduction and gating in influenza M2 proton channels from solid-state NMR
- PMID: 20966251
- PMCID: PMC4102303
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1191714
Mechanisms of proton conduction and gating in influenza M2 proton channels from solid-state NMR
Abstract
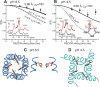
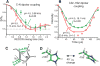
The M2 protein of influenza viruses forms an acid-activated tetrameric proton channel. We used solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to determine the structure and functional dynamics of the pH-sensing and proton-selective histidine-37 in M2 bound to a cholesterol-containing virus-envelope-mimetic membrane so as to better understand the proton conduction mechanism. In the high-pH closed state, the four histidines form an edge-face π-stacked structure, preventing the formation of a hydrogen-bonded water chain to conduct protons. In the low-pH conducting state, the imidazoliums hydrogen-bond extensively with water and undergo microsecond ring reorientations with an energy barrier greater than 59 kilojoules per mole. This barrier is consistent with the temperature dependence of proton conductivity, suggesting that histidine-37 dynamically shuttles protons into the virion. We propose a proton conduction mechanism in which ring-flip-assisted imidazole deprotonation is the rate-limiting step.
Figures


Comment in
-
Structural biology. The flu's proton escort.Science. 2010 Oct 22;330(6003):456-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1197748. Science. 2010. PMID: 20966238 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

