The ligase PIAS1 restricts natural regulatory T cell differentiation by epigenetic repression
- PMID: 20966256
- PMCID: PMC3043201
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1193787
The ligase PIAS1 restricts natural regulatory T cell differentiation by epigenetic repression
Abstract
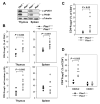
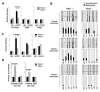
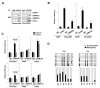
CD4(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T (T(reg)) cells are important for maintaining immune tolerance. Understanding the molecular mechanism that regulates T(reg) differentiation will facilitate the development of effective therapeutic strategies against autoimmune diseases. We report here that the SUMO E3 ligase PIAS1 restricts the differentiation of natural T(reg) cells by maintaining a repressive chromatin state of the Foxp3 promoter. PIAS1 acts by binding to the Foxp3 promoter to recruit DNA methyltransferases and heterochromatin protein 1 for epigenetic modifications. Pias1 deletion caused promoter demethylation, reduced histone H3 methylation at Lys(9), and enhanced promoter accessibility. Consistently, Pias1(-/-) mice displayed an increased natural T(reg) cell population and were resistant to the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Our studies have identified an epigenetic mechanism that negatively regulates the differentiation of natural T(reg) cells.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

