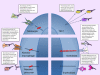
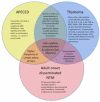
Immunodeficiency secondary to anticytokine autoantibodies
- PMID: 20966748
- PMCID: PMC3132574
- DOI: 10.1097/ACI.0b013e3283402b41
Immunodeficiency secondary to anticytokine autoantibodies
Abstract
Purpose of review: Anticytokine autoantibodies are an important and emerging mechanism of disease pathogenesis. We will review the clinical and laboratory features of syndromes in which immunodeficiency is caused by or associated with neutralizing anticytokine autoantibodies.
Recent findings: A growing number of patients have been described who demonstrate unique infectious phenotypes associated with neutralizing autoantibodies that target a particular cytokine known to participate in host defense against the offending organism. Examples include antigranulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) autoantibodies and pulmonary alveolar proteinosis; anti-interferon (IFN)-γ autoantibodies and disseminated nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM); anti-interleukin-(IL)-6 autoantibodies and severe staphylococcal skin infection; anti-IL-17A, anti-IL-17F, or anti-IL-22 autoantibodies in patients with mucocutaneous candidiasis in the setting of both the autoimmune polyendocrinopathy, candidiasis, ectodermal dystrophy (APECED) syndrome and in cases of thymoma.
Summary: Anticytokine autoantibodies have manifestations that are diverse, ranging from asymptomatic to life-threatening. These emerging and fascinating causes of acquired immunodeficiency may explain some previously idiopathic syndromes.
Figures
References
-
- Uchida K, Beck DC, Yamamoto T, Berclaz PY, Abe S, Staudt MK, Carey BC, Filippi MD, Wert SE, Denson LA, et al. GM-CSF autoantibodies and neutrophil dysfunction in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:567–579. - PubMed
-
- Trapnell BC, Whitsett JA, Nakata K. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2527–2539. - PubMed
-
-
Kisand K, Wolff AS Boe, Podkrajsek KT, Tserel L, Link M, Kisand KV, Ersvaer E, Perheentupa J, Erichsen MM, Bratanic N, et al. Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis in APECED or thymoma patients correlates with autoimmunity to Th17-associated cytokines. J Exp Med. 2010;207:299–308. This was one of the first 2 papers identifying anti-IL-17A, IL-17F and and IL-22 autoantibodies in strong association with candidiasis seen in APECED syndrome and in 2 patients with thymoma and CMC.
-
-
-
Puel A, Doffinger R, Natividad A, Chrabieh M, Barcenas-Morales G, Picard C, Cobat A, Ouachee-Chardin M, Toulon A, Bustamante J, et al. Autoantibodies against IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22 in patients with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis and autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I. J Exp Med. 2010;207:291–297. This was one of the first 2 papers identifying anti-IL-17A, IL-17F and and IL-22 autoantibodies in strong association with candidiasis seen in APECED syndrome
-
-
-
Riches PL, McRorie E, Fraser WD, Determann C, van’t Hof R, Ralston SH. Osteoporosis associated with neutralizing autoantibodies against osteoprotegerin. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1459–1465. This paper is the first report of severe osteoporosis associated with anti-osteoprotegerin autoantibodies in celiac disease. It underscores the diverse range of phenotypes that may be caused by autoantibodies to endogenous factors.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials