Tomographic molecular imaging of x-ray-excitable nanoparticles
- PMID: 20967061
- PMCID: PMC12121645
- DOI: 10.1364/OL.35.003345
Tomographic molecular imaging of x-ray-excitable nanoparticles
Abstract
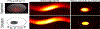
X-ray luminescence computed tomography (XLCT) is proposed as a new dual molecular/anatomical imaging modality. XLCT is based on the selective excitation and optical detection of x-ray-excitable nanoparticles. As a proof of concept, we built a prototype XLCT system and imaged near-IR-emitting Gd(2)O(2)S:Eu phosphors in various phantoms. Imaging in an optically diffusive medium shows that imaging performance is not affected by optical scatter; furthermore, the linear response of the reconstructed images suggests that XLCT is capable of quantitative imaging.
Figures




References
-
- Speck U, in Molecular Imaging I (Springer, 2008), pp. 167–175.
-
- Xing M, Cao W, Pang T, Ling X, and Chen N, Chin. Sci. Bull 54, 2982 (2009).
-
- Tian Y, Cao W-H, Luo X-X, and Fu Y, J. Alloys Compd 433, 313 (2007).
-
- Sun C, Carpenter C, Pratx G, and Xing L, in World Molecular Imaging Congress (2010).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

