Motor neuron trophic factors: therapeutic use in ALS?
- PMID: 20971133
- PMCID: PMC3109102
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2010.10.003
Motor neuron trophic factors: therapeutic use in ALS?
Abstract
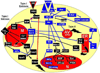
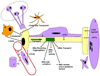
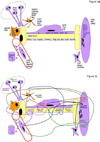
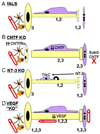
The modest effects of neurotrophic factor (NTF) treatment on lifespan in both animal models and clinical studies of Amyotropic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) may result from any one or combination of the four following explanations: 1.) NTFs block cell death in some physiological contexts but not in ALS; 2.) NTFs do not rescue motoneurons (MNs) from death in any physiological context; 3.) NTFs block cell death in ALS but to no avail; and 4.) NTFs are physiologically effective but limited by pharmacokinetic constraints. The object of this review is to critically evaluate the role of both NTFs and the intracellular cell death pathway itself in regulating the survival of spinal and cranial (lower) MNs during development, after injury and in response to disease. Because the role of molecules mediating MN survival has been most clearly resolved by the in vivo analysis of genetically engineered mice, this review will focus on studies of such mice expressing reporter, null or other mutant alleles of NTFs, NTF receptors, cell death or ALS-associated genes.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Hamburger V. Regression versus peripheral control of differentiation in motor hypoplasia. Am J Anat. 1958;102(3):365–409. - PubMed
-
- Purves D. Body and brain: a trophic theory of neural connections. Cambridge, UK: Harvard UP; 1988. - PubMed
-
- Ellis RE, Yuan JY, Horvitz HR. Mechanisms and functions of cell death. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:663–698. - PubMed
-
- Oppenheim RW. Cell death during development of the nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:453–501. - PubMed
-
- Appel SH. A unifying hypothesis for the cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, parkinsonism, and Alzheimer disease. Ann Neurol. 1981;10(6):499–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

