Emergency orthogeriatrics: concepts and therapeutic alternatives
- PMID: 20971398
- PMCID: PMC3217215
- DOI: 10.1016/j.emc.2010.06.005
Emergency orthogeriatrics: concepts and therapeutic alternatives
Abstract
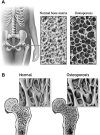
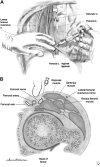
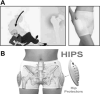
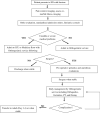
Multidisciplinary orthogeriatric care can enhance prompt ED diagnosis, optimal pre- and postoperative care, and functional recovery in older adults with bony injuries. Emergency care providers should be cognizant of prevalent geriatric syndromes including delirium and standing level falls to minimize fracture-related morbidity. Recognizing the implications of aging physiology, acute care physicians should be aware of effective alternatives to analgesia, procedural sedation, and definitive imaging to promote early surgical management and postoperative recovery.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Roberts DC, McKay MP, Shaffer A. Increasing rates of emergency department visits for elderly patients in the United States, 1993 to 2003. Ann Emerg Med. 2008;51:769–74. - PubMed
-
- Downing A, Wilson R. Older people's use of accident and emergency services. Age Ageing. 2005;34:24–30. - PubMed
-
- McNamara RM, Rousseau E, Sanders AB. Geriatric emergency medicine: a survey of practicing emergency physicians. Ann Emerg Med. 1992;21:796–801. - PubMed
-
- Lips P. Epidemiology and predictors of fractures associated with osteoporosis. Am J Med. 1997;103:3S–8S. - PubMed
-
- Carter MW, Gupta S. Characteristics and outcomes of injury-related ED visits among older adults. Am J Emerg Med. 2008;26:296–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

