Identifying and validating biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 20971518
- PMCID: PMC3016495
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2010.09.007
Identifying and validating biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
The identification and validation of biomarkers for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease (AD) and other forms of dementia are increasingly important. To date, ELISA measurement of β-amyloid(1-42), total tau and phospho-tau-181 in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is the most advanced and accepted method to diagnose probable AD with high specificity and sensitivity. However, it is a great challenge to search for novel biomarkers in CSF and blood by using modern potent methods, such as microarrays and mass spectrometry, and to optimize the handling of samples (e.g. collection, transport, processing, and storage), as well as the interpretation using bioinformatics. It seems likely that only a combined analysis of several biomarkers will define a patient-specific signature to diagnose AD in the future.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
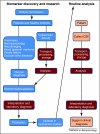
References
-
- Frey H.J. Problems associated with biological markers of Alzheimer's disease. Neurochemical Res. 2005;30:1501–1510. - PubMed
-
- Henley S.M.D. Biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2005;18:698–705. - PubMed
-
- Sprott R.L. Biomarkers of aging and disease: introduction and definitions. Exp. Gerontol. 2010;45:2–4. - PubMed
-
- Cedazo-Minguez A. Biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia: clinical needs, limitations and future aspects. Exp. Gerontol. 2010;45:5–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

