Deciphering the role of glucosamine-6-phosphate in the riboswitch action of glmS ribozyme
- PMID: 20971809
- PMCID: PMC2995406
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2334110
Deciphering the role of glucosamine-6-phosphate in the riboswitch action of glmS ribozyme
Abstract
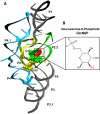
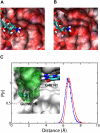
The GlmS ribozyme is believed to exploit a general acid-base catalytic mechanism in the presence of glucosamine-6-phosphate (GlcN6P) to accelerate self-cleavage by approximately six orders of magnitude. The general acid and general base are not known, and the role of the GlcN6P cofactor is even less well understood. The amine group of GlcN6P has the ability to either accept or donate a proton and could therefore potentially act as an acid or a base. In order to decipher the role of GlcN6P in the self-cleavage of glmS, we have determined the preferred protonation state of the amine group in the wild-type and an inactive G40A mutant using molecular dynamics simulations and free energy calculations. Here we show that, upon binding of GlcN6P to wild-type glmS, the pK(a) of the amine moiety is altered by the active site environment, decreasing by about 2.2 from a solution pK(a) of about 8.2. On the other hand, we show that the pK(a) of the amine group slightly increases to about 8.4 upon binding to the G40A inactive mutant of glmS. These results suggest that GlcN6P acts as a general acid in the self-cleavage of glmS. Upon binding to glmS, GlcN6P can easily release a proton to the 5'-oxygen of G1 during self-cleavage of the backbone phosphodiester bond. However, in the G40A inactive mutant of glmS, the results suggest that the ability of GlcN6P to easily release its proton is diminished, in addition to the possible lack of G40 as an effective base.
Figures



References
-
- Allison S, Xin Y 2006. Electrokinetic transport of a spherical gel-layer model particle: Inclusion of charge regulation and application to polystyrene sulfonate. J Colloid Interface Sci 299: 977–988 - PubMed
-
- Anderson CF, Record MT 1995. Salt nucleic-acid interactions. Annu Rev Phys Chem 46: 657–700 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
