IL-9 governs allergen-induced mast cell numbers in the lung and chronic remodeling of the airways
- PMID: 20971830
- PMCID: PMC3385369
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200909-1462OC
IL-9 governs allergen-induced mast cell numbers in the lung and chronic remodeling of the airways
Abstract
Rationale: IL-9 is a pleiotropic cytokine that has multiple effects on structural as well as numerous hematopoietic cells, which are central to the pathogenesis of asthma.
Objectives: The contribution of IL-9 to asthma pathogenesis has thus far been unclear, due to conflicting reports in the literature. These earlier studies focused on the role of IL-9 in acute inflammatory models; here we have investigated the effects of IL-9 blockade during chronic allergic inflammation.
Methods: Mice were exposed to either prolonged ovalbumin or house dust mite allergen challenge to induce chronic inflammation and airway remodeling.
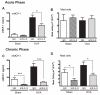
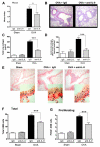
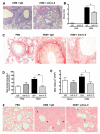
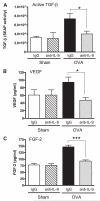
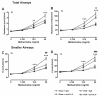
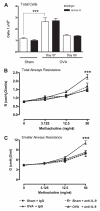
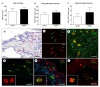
Measurements and main results: We found that IL-9 governs allergen-induced mast cell (MC) numbers in the lung and has pronounced effects on chronic allergic inflammation. Anti-IL-9 antibody-treated mice were protected from airway remodeling with a concomitant reduction in mature MC numbers and activation, in addition to decreased expression of the profibrotic mediators transforming growth factor-β1, vascular endothelial growth factor, and fibroblast growth factor-2 in the lung. Airway remodeling was associated with impaired lung function in the peripheral airways and this was reversed by IL-9 neutralization. In human asthmatic lung tissue, we identified MCs as the main IL-9 receptor expressing population and found them to be sources of vascular endothelial growth factor and fibroblast growth factor-2.
Conclusions: Our data suggest an important role for an IL-9-MC axis in the pathology associated with chronic asthma and demonstrate that an impact on this axis could lead to a reduction in chronic inflammation and improved lung function in patients with asthma.
Figures
Comment in
-
Revolution 9: the backwards and forwards evidence surrounding interleukin-9.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Apr 1;183(7):834-5. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201009-1464ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011. PMID: 21471072 No abstract available.
References
-
- Holgate ST. Pathogenesis of asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008;38:872–897. - PubMed
-
- McMillan SJ, Xanthou G, Lloyd CM. Manipulation of allergen-induced airway remodeling by treatment with anti-TGF-b antibody: effect on the Smad signaling pathway. J Immunol. 2005;174:5774–5780. - PubMed
-
- Postma DS, Bleecker ER, Amelung PJ, Holroyd KJ, Xu J, Panhuysen CIM, Meyers DA, Levitt RC. Genetic susceptibility to asthma-bronchial hyperresponsiveness coinherited with a major gene for atopy. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:894–900. - PubMed
-
- McLane MP, Haczku A, van de Rijn M, Weiss C, Ferrante V, MacDonald D, Renauld JC, Nicolaides NC, Holroyd KJ, Levitt RC. Interleukin-9 promotes allergen-induced eosinophilic inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in transgenic mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998;19:713–720. - PubMed

