Effect of sulfadiazine-contaminated pig manure on the abundances of genes and transcripts involved in nitrogen transformation in the root-rhizosphere complexes of maize and clover
- PMID: 20971872
- PMCID: PMC3008267
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01252-10
Effect of sulfadiazine-contaminated pig manure on the abundances of genes and transcripts involved in nitrogen transformation in the root-rhizosphere complexes of maize and clover
Abstract
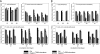
The antibiotic sulfadiazine (SDZ) can enter the environment by application of manure from antibiotic-treated animals to arable soil. Because antibiotics are explicitly designed to target microorganisms, they likely affect microbes in the soil ecosystem, compromising important soil functions and disturbing processes in nutrient cycles. In a greenhouse experiment, we investigated the impact of sulfadiazine-contaminated pig manure on functional microbial communities involved in key processes of the nitrogen cycle in the root-rhizosphere complexes (RRCs) of maize (Zea mays) and clover (Trifolium alexandrinum). At both the gene and transcript level, we performed real-time PCR using nifH, amoA (in both ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea), nirK, nirS, and nosZ as molecular markers for nitrogen fixation, nitrification, and denitrification. Sampling was performed 10, 20, and 30 days after the application. SDZ affected the abundance pattern of all investigated genes in the RRCs of both plant species (with stronger effects in the RRC of clover) 20 and 30 days after the addition. Surprisingly, effects on the transcript level were less pronounced, which might indicate that parts of the investigated functional groups were tolerant or resistant against SDZ or, as in the case of nifH and clover, have been protected by the nodules.
Figures

References
-
- Alcock, R. E., A. Sweetman, and K. C. Jones. 1999. Assessment of organic contaminant fate in waste water treatment plants I: selected compounds and physicochemical properties. Chemosphere 38:2247-2262. - PubMed
-
- Antignac, J. P., B. Le Bizec, F. Monteau, and F. Andre. 2003. Validation of analytical methods based on mass spectrometric detection according to the “2002/657/EC” European decision: guideline and application. Anal. Chim. Acta 483:325-334.
-
- Bais, H. P., T. L. Weir, L. G. Perry, S. Gilroy, and J. M. Vivanco. 2006. The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interactions with plants and other organisms. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 57:233-266. - PubMed
-
- Balaban, N. Q., J. Merrin, R. Chait, L. Kowalik, and S. Leibler. 2004. Bacterial persistence as a phenotypic switch. Science 305:1622-1625. - PubMed
-
- Bartossek, R., G. W. Nicol, A. Lanzen, H. P. Klenk, and C. Schleper. 2010. Homologues of nitrite reductases in ammonia-oxidizing archaea: diversity and genomic context. Environ. Microbiol. 12:1075-1088. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

