Meta-analysis of three genome-wide association studies identifies susceptibility loci for colorectal cancer at 1q41, 3q26.2, 12q13.13 and 20q13.33
- PMID: 20972440
- PMCID: PMC5098601
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.670
Meta-analysis of three genome-wide association studies identifies susceptibility loci for colorectal cancer at 1q41, 3q26.2, 12q13.13 and 20q13.33
Abstract
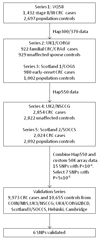
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified ten loci harboring common variants that influence risk of developing colorectal cancer (CRC). To enhance the power to identify additional CRC risk loci, we conducted a meta-analysis of three GWAS from the UK which included a total of 3,334 affected individuals (cases) and 4,628 controls followed by multiple validation analyses including a total of 18,095 cases and 20,197 controls. We identified associations at four new CRC risk loci: 1q41 (rs6691170, odds ratio (OR) = 1.06, P = 9.55 × 10⁻¹⁰ and rs6687758, OR = 1.09, P = 2.27 × 10⁻⁹, 3q26.2 (rs10936599, OR = 0.93, P = 3.39 × 10⁻⁸), 12q13.13 (rs11169552, OR = 0.92, P = 1.89 × 10⁻¹⁰ and rs7136702, OR = 1.06, P = 4.02 × 10⁻⁸) and 20q13.33 (rs4925386, OR = 0.93, P = 1.89 × 10⁻¹⁰). In addition to identifying new CRC risk loci, this analysis provides evidence that additional CRC-associated variants of similar effect size remain to be discovered.
Conflict of interest statement
statement The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Pritchard JK, Cox NJ. The allelic architecture of human disease genes: common disease-common variant…or not? Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11:2417–23. - PubMed
-
- Tomlinson I, et al. A genome-wide association scan of tag SNPs identifies a susceptibility variant for colorectal cancer at 8q24.21. Nat Genet. 2007;39:984–8. - PubMed
-
- Zanke BW, et al. Genome-wide association scan identifies a colorectal cancer susceptibility locus on chromosome 8q24. Nat Genet. 2007;39:989–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- G0301096/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- A10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- G0000657-53203/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CZB/4/449/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MR/K001744/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U122861325/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- A10119/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- MC_U127527198/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 10119/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom

