Recent epidemiology of Clostridium difficile infection during hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- PMID: 20973823
- PMCID: PMC3860287
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2010.01331.x
Recent epidemiology of Clostridium difficile infection during hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Abstract
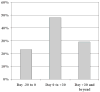
Given the limited information on Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) during hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), we examined the recent epidemiology of CDI in HSCT recipients at our institution. During the two-yr retrospective study period (2005-2006), 361 transplants were performed: 60% allogeneic and 40% autologous. Among all hospitalized patients in a non-outbreak setting, CDI rates in HSCT recipients were ninefold higher than those in general patients and 1.4-fold higher than those in patients with cancer (24.0 vs. 2.6 vs. 16.8/10,000 patient-days respectively). Sixty-two episodes of CDI occurred in 51 (14%) HSCT recipients: 39 (18%) allogeneic vs. 12 (8%) autologous (p = 0.01). Almost half of CDI episodes occurred within 30 d post-HSCT and 22% before HSCT. Clostridium difficile toxin assay was initially positive in 28% of the first, 31% of the second and 27% of the third stool samples tested. All but one patient responded to therapy with metronidazole or vancomycin. Severe CDI occurred in one patient and recurrent CDI in two patients. CDI is common during HSCT especially in allogeneic transplants during the peri-HSCT period. Prospective studies to better define the epidemiology and identify unique risk factors for CDI and more accurate tests to confirm the diagnosis in this population are needed.
© 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None of the authors have any conflict of interest related to this study.
Figures
References
-
- Bobak D, Arfons LM, Creger RJ, Lazarus HM. Clostridium difficile-associated disease in human stem cell transplant recipients: coming epidemic or false alarm? Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008;42:705. - PubMed
-
- Avery R, Pohlman B, Adal K, et al. High prevalence of diarrhea but infrequency of documented Clostridium difficile in autologous peripheral blood progenitor cell transplant recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000;25:67. - PubMed
-
- Tomblyn M, Gordon L, Singhal S, et al. Rarity of toxigenic Clostridium difficile infections after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: implications for symptomatic management of diarrhea. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002;30:517. - PubMed
-
- McDonald LC, Killgore GE, Thompson A, et al. An epidemic, toxin gene-variant strain of Clostridium difficile. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical