Chronic alcohol consumption decreases the percentage and number of NK cells in the peripheral lymph nodes and exacerbates B16BL6 melanoma metastasis into the draining lymph nodes
- PMID: 20974468
- PMCID: PMC3006065
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2010.10.001
Chronic alcohol consumption decreases the percentage and number of NK cells in the peripheral lymph nodes and exacerbates B16BL6 melanoma metastasis into the draining lymph nodes
Abstract
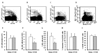
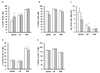
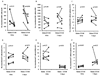
NK cells in the lymph nodes play important roles in inhibiting tumor metastasis into draining lymph nodes. Previously, we reported that chronic alcohol consumption interferes with NK cell trafficking from the bone marrow to the spleen. Herein, we found that alcohol consumption decreases the numbers of NK cells in lymph nodes. Adoptive transfer experiments indicated that continued exposure of donor splenocytes to alcohol inhibits NK but not T cell trafficking to lymph nodes. Alcohol did not negatively affect CCR7(+) and CXCR3(+) NK cells, but decreased the percentage and number of CD62L(+) NK cells in the spleen, which are an important source of NK cell trafficking into the lymph nodes. These data suggest that modulation of the microenvironment associated with alcohol consumption impairs the trafficking of NK cells to lymph nodes. The decreased number of NK cells in the lymph nodes was associated with increased melanoma metastasis into the draining lymph nodes.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Chronic alcohol consumption impairs distribution and compromises circulation of B cells in B16BL6 melanoma-bearing mice.J Immunol. 2012 Aug 1;189(3):1340-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200442. Epub 2012 Jun 29. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22753935 Free PMC article.
-
The modulation of B16BL6 melanoma metastasis is not directly mediated by cytolytic activity of natural killer cells in alcohol-consuming mice.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000 Jun;24(6):837-44. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000. PMID: 10888072
-
Chronic alcohol consumption perturbs the balance between thymus-derived and bone marrow-derived natural killer cells in the spleen.J Leukoc Biol. 2008 Jan;83(1):41-7. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0707472. Epub 2007 Sep 28. J Leukoc Biol. 2008. PMID: 17906116
-
Suppression of tumor formation in lymph nodes by L-selectin-mediated natural killer cell recruitment.J Exp Med. 2005 Dec 19;202(12):1679-89. doi: 10.1084/jem.20051473. Epub 2005 Dec 13. J Exp Med. 2005. PMID: 16352740 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cell activity in patients with carcinoma of the larynx and hypopharynx.Laryngoscope. 1985 Nov;95(11):1391-400. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198511000-00020. Laryngoscope. 1985. PMID: 3903404 Review.
Cited by
-
Alcohol remodels the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment by targeting myeloid-derived suppressor cells.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 May 15;13(5):1786-1805. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37293168 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of mRNA expression differences in bladder cancer metastasis based on TCGA datasets.J Int Med Res. 2021 Mar;49(3):300060521996929. doi: 10.1177/0300060521996929. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33787386 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Alcohol on Tumor Growth, Metastasis, Immune Response, and Host Survival.Alcohol Res. 2015;37(2):311-22. Alcohol Res. 2015. PMID: 26695753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential Role of IFN-γ in Regulating Gut Antimicrobial Peptides and Microbiota to Protect Against Alcohol-Induced Bacterial Translocation and Hepatic Inflammation in Mice.Front Physiol. 2021 Jan 18;11:629141. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.629141. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33536944 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic alcohol consumption impairs distribution and compromises circulation of B cells in B16BL6 melanoma-bearing mice.J Immunol. 2012 Aug 1;189(3):1340-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200442. Epub 2012 Jun 29. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22753935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yokoyama WM, Plougastel BF. Immune functions encoded by the natural killer gene complex. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003;3:304–316. - PubMed
-
- Chalifour A, Jeannin P, Gauchat JF, Blaecke A, Malissard M, N'Guyen T, Thieblemont N, Delneste Y. Direct bacterial protein PAMP recognition by human NK cells involves TLRs and triggers alpha-defensin production. Blood. 2004;104:1778–1783. - PubMed
-
- Martin-Fontecha A, Thomsen LL, Brett S, Gerard C, Lipp M, Lanzavecchia A, Sallusto F. Induced recruitment of NK cells to lymph nodes provides IFN-gamma for T(H)1 priming. Nat. Immunol. 2004;5:1260–1265. - PubMed
-
- Walzer T, Chiossone L, Chaix J, Calver A, Carozzo C, Garrigue-Antar L, Jacques Y, Baratin M, Tomasello E, Vivier E. Natural killer cell trafficking in vivo requires a dedicated sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor. Nat. Immunol. 2007;8:1337–1344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

