Developmental change in young children's use of haptic information in a visual task: the role of hand movements
- PMID: 20974476
- PMCID: PMC2991392
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jecp.2010.09.004
Developmental change in young children's use of haptic information in a visual task: the role of hand movements
Abstract
Preschoolers who explore objects haptically often fail to recognize those objects in subsequent visual tests. This suggests that children may represent qualitatively different information in vision and haptics and/or that children's haptic perception may be poor. In this study, 72 children (2½-5 years of age) and 20 adults explored unfamiliar objects either haptically or visually and then chose a visual match from among three test objects, each matching the exemplar on one perceptual dimension. All age groups chose shape-based matches after visual exploration. Both 5-year-olds and adults also chose shape-based matches after haptic exploration, but younger children did not match consistently in this condition. Certain hand movements performed by children during haptic exploration reliably predicted shape-based matches but occurred at very low frequencies. Thus, younger children's difficulties with haptic-to-visual information transfer appeared to stem from their failure to use their hands to obtain reliable haptic information about objects.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
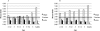
References
-
- Abravanel E. Intersensory Integration of Spatial Position During Early Childhood. Perceptual and Motor Skills. 1968;26(1):251–256. - PubMed
-
- Abravanel E. Choice for Shape Vs Textural Matching by Young Children. Perceptual and Motor Skills. 1970;31(2):527–533. - PubMed
-
- Abravanel E. Active Detection of Solid-Shape Information by Touch and Vision. Perception & Psychophysics. 1971;10(5):358–360.
-
- Abravanel E. Short-Term Memory for Shape Information Processed Intramodally and Intermodally at 3 Ages. Perceptual and Motor Skills. 1972;35(2):419–425. - PubMed
-
- Abravanel E. Division of Labor between Hand and Eye When Perceiving Shape. Neuropsychologia. 1973;11(7):207–211. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

