Building mitotic chromosomes
- PMID: 20974528
- PMCID: PMC3060342
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2010.09.009
Building mitotic chromosomes
Abstract
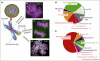
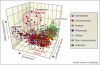
Mitotic chromosomes are the iconic structures into which the genome is packaged to ensure its accurate segregation during mitosis. Although they have appeared on countless journal cover illustrations, there remains no consensus on how the chromatin fiber is packaged during mitosis. In fact, work in recent years has both added to existing controversies and sparked new ones. By contrast, there has been very significant progress in determining the protein composition of isolated mitotic chromosomes. Here, we discuss recent studies of chromosome organization and provide an in depth description of the latest proteomics studies, which have at last provided us with a definitive proteome for vertebrate chromosomes.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Maiato H., Deluca J., Salmon E.D., Earnshaw W.C. The dynamic kinetochore-microtubule interface. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:5461–5477. - PubMed
-
- Cheeseman I.M., Desai A. Molecular architecture of the kinetochore-microtubule interface. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:33–46. - PubMed
-
- de Lange T. Shelterin: the protein complex that shapes and safeguards human telomeres. Genes Dev. 2005;19:2100–2110. - PubMed
-
- Palm W., de Lange T. How shelterin protects mammalian telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 2008;42:301–334. - PubMed
-
- Sharp L.W. Structure of large somatic chromosomes. Botanical Gazette. 1929;88:349–382.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

