Tumorigenicity of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells lacking the p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase
- PMID: 20974639
- PMCID: PMC3242445
- DOI: 10.1677/JOE-10-0237
Tumorigenicity of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells lacking the p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase
Abstract
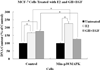
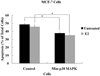
We have generated cell lines with significantly reduced expression of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK), Min-p38 MAPK cells, and used these cells to investigate p38 MAPK's role in tumorigenesis of breast cancer cells. MCF-7 cells were stably transfected with a plasmid producing small interfering RNA that inhibited the expression of p38 MAPK. Control cells were stably transfected with the same plasmid producing non-interfering RNA. The reduction in the p38 MAPK activity caused a significant increase in the expressions of estrogen receptor-α (ERα) and the progesterone receptor, but eliminated the expression of ERβ. Min-p38 MAPK cells showed an enhanced overall growth response to 17β-estradiol (E₂), whereas GH plus epidermal growth factor were largely ineffective growth stimulators in these cells compared to controls. Although the long-term net growth rate of the Min-p38 MAPK cells was increased in response to E₂, their proliferation rate was lower compared to controls in short-term cultures. However, the Min-p38 MAPK cells did show a significant decreased rate of apoptosis after E₂ treatment and a reduction in the basal phosphorylation of p53 tumor suppressor protein compared to controls. When the Min-p38 MAPK cells were xenografted into E₂-treated athymic nude mice, their tumorigenicity was enhanced compared to control cells. Increased tumorigenicity of Min-p38 MAPK cells was caused mainly by a decrease in the apoptosis rate indicating that the lack of the p38 MAPK caused an imbalance to increase the ERα:ERβ ratio and a reduction in the activity of the p53 tumor suppressor protein.
Figures






References
-
- Acconcia F, Totta P, Ogawa S, Cardillo I, Inoue S, Leone S, Trentalance A, Muramatsu M, Marino M. Survival versus apoptotic 17β-estradiol effect: role of ERα and ERβ activated non-genomic signaling. Journal of Cell Physiology. 2005;203:195–201. - PubMed
-
- Bulavin DV, Fornace AJ., Jr p38 MAP kinase’s emerging role as a tumor suppressor. Advances in Cancer Research. 2004;92:95–118. - PubMed
-
- Caiazza F, Galluzzo P, Lorenzetti S, Marino M. 17β-estradiol induces ERβ up-regulation via p38/MAPK activation in colon cancer cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2007;359:102–107. - PubMed
-
- Casey G, Lo-Hsueh M, Lopez ME, Vogelstein B, Stanbridge EJ. Growth suppression of human breast cancer cells by the introduction of a wild-type p53 gene. Oncogene. 1991;6:1791–1797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

