Rapamycin, but not resveratrol or simvastatin, extends life span of genetically heterogeneous mice
- PMID: 20974732
- PMCID: PMC3021372
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glq178
Rapamycin, but not resveratrol or simvastatin, extends life span of genetically heterogeneous mice
Abstract
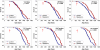
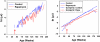
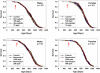
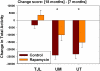
Rapamycin was administered in food to genetically heterogeneous mice from the age of 9 months and produced significant increases in life span, including maximum life span, at each of three test sites. Median survival was extended by an average of 10% in males and 18% in females. Rapamycin attenuated age-associated decline in spontaneous activity in males but not in females. Causes of death were similar in control and rapamycin-treated mice. Resveratrol (at 300 and 1200 ppm food) and simvastatin (12 and 120 ppm) did not have significant effects on survival in male or female mice. Further evaluation of rapamycin's effects on mice is likely to help delineate the role of the mammalian target of rapamycin complexes in the regulation of aging rate and age-dependent diseases and may help to guide a search for drugs that retard some or all of the diseases of aging.
Figures



References
-
- Miller RA, Harrison DE, Astle CM, et al. An aging interventions testing program: study design and interim report. Aging Cell. 2007;6:565–575. - PubMed
-
- Wang C, Li Q, Redden DT, Weindruch R, Allison DB. Statistical methods for testing effects on “maximum lifespan”. Mech Ageing Dev. 2004;125:629–632. - PubMed
-
- Promislow DE, Tatar M, Pletcher SD, Carey J. Below-threshold mortality and its impact on studies in evolutionary ecology. J Evol Biol. 1999;12:314–328.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 AG029313/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG027916/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG028730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG022303/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG022308/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG025707/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG038070/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21-AG029313/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG022303/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG024824/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019719/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG022307/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

