RiboSys, a high-resolution, quantitative approach to measure the in vivo kinetics of pre-mRNA splicing and 3'-end processing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 20974745
- PMCID: PMC2995417
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2162610
RiboSys, a high-resolution, quantitative approach to measure the in vivo kinetics of pre-mRNA splicing and 3'-end processing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
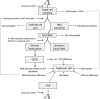
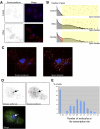
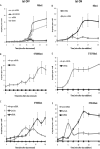
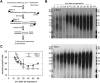
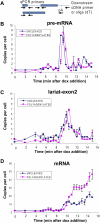
We describe methods for obtaining a quantitative description of RNA processing at high resolution in budding yeast. As a model gene expression system, we constructed tetON (for induction studies) and tetOFF (for repression, derepression, and RNA degradation studies) yeast strains with a series of reporter genes integrated in the genome under the control of a tetO7 promoter. Reverse transcription and quantitative real-time-PCR (RT-qPCR) methods were adapted to allow the determination of mRNA abundance as the average number of copies per cell in a population. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) measurements of transcript numbers in individual cells validated the RT-qPCR approach for the average copy-number determination despite the broad distribution of transcript levels within a population of cells. In addition, RT-qPCR was used to distinguish the products of the different steps in splicing of the reporter transcripts, and methods were developed to map and quantify 3'-end cleavage and polyadenylation. This system permits pre-mRNA production, splicing, 3'-end maturation and degradation to be quantitatively monitored with unprecedented kinetic detail, suitable for mathematical modeling. Using this approach, we demonstrate that reporter transcripts are spliced prior to their 3'-end cleavage and polyadenylation, that is, cotranscriptionally.
Figures


References
-
- Belli G, Gari E, Aldea M, Herrero E 1998a. Functional analysis of yeast essential genes using a promoter-substitution cassette and the tetracycline-regulatable dual expression system. Yeast 14: 1127–1138 - PubMed
-
- Blake WJ, Balazsi G, Kohanski MA, Isaacs FJ, Murphy KF, Kuang Y, Cantor CR, Walt DR, Collins JJ 2006. Phenotypic consequences of promoter-mediated transcriptional noise. Mol Cell 24: 853–865 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
