Short RNA duplexes guide sequence-dependent cleavage by human Dicer
- PMID: 20974746
- PMCID: PMC2995407
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2346510
Short RNA duplexes guide sequence-dependent cleavage by human Dicer
Abstract
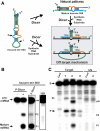
Dicer is a member of the double-stranded (ds) RNA-specific ribonuclease III (RNase III) family that is required for RNA processing and degradation. Like most members of the RNase III family, Dicer possesses a dsRNA binding domain and cleaves long RNA duplexes in vitro. In this study, Dicer substrate selectivity was examined using bipartite substrates. These experiments revealed that an RNA helix possessing a 2-nucleotide (nt) 3'-overhang may bind and direct sequence-specific Dicer-mediated cleavage in trans at a fixed distance from the 3'-end overhang. Chemical modifications of the substrate indicate that the presence of the ribose 2'-hydroxyl group is not required for Dicer binding, but some located near the scissile bonds are needed for RNA cleavage. This suggests a flexible mechanism for substrate selectivity that recognizes the overall shape of an RNA helix. Examination of the structure of natural pre-microRNAs (pre-miRNAs) suggests that they may form bipartite substrates with complementary mRNA sequences, and thus induce seed-independent Dicer cleavage. Indeed, in vitro, natural pre-miRNA directed sequence-specific Dicer-mediated cleavage in trans by supporting the formation of a substrate mimic.
Figures



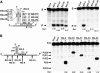

References
-
- Carbonell A, Martinez de Alba AE, Flores R, Gago S 2008. Double-stranded RNA interferes in a sequence-specific manner with the infection of representative members of the two viroid families. Virology 371: 44–53 - PubMed
-
- Carmell MA, Hannon GJ 2004. RNase III enzymes and the initiation of gene silencing. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11: 214–218 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
