The tumor-associated EpCAM regulates morphogenetic movements through intracellular signaling
- PMID: 20974811
- PMCID: PMC3003323
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201004074
The tumor-associated EpCAM regulates morphogenetic movements through intracellular signaling
Abstract
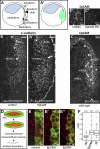
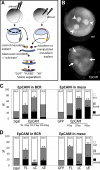
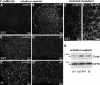
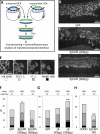
Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) is best known as a tumor-associated protein highly expressed in carcinomas. The function of this cell surface protein during embryonic development and its potential role in cancer are still poorly understood. We identified EpCAM in a gain-of-function screen for inducers of abnormal tissue mixing during gastrulation. Elevated EpCAM levels in either the ectoderm or the mesoderm confer "invasive" properties to cells in both populations. We found that this phenotype represents an "overstimulation" of an essential activity of EpCAM in controlling cell movements during embryonic development. Surprisingly, this property is independent of the putative adhesive function of EpCAM, and rather relies on a novel signaling function that operates through down-regulation of PKC activity. We show that inhibition of novel PKCs accounts entirely for the invasive phenotype induced by abnormally high levels of EpCAM as well as for its normal function in regulating cell rearrangement during early development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EpCAM as Modulator of Tissue Plasticity.Cells. 2020 Sep 19;9(9):2128. doi: 10.3390/cells9092128. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32961790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EpCAM controls actomyosin contractility and cell adhesion by direct inhibition of PKC.Dev Cell. 2013 Nov 11;27(3):263-77. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.10.003. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Dev Cell. 2013. PMID: 24183651
-
EpCAM is involved in maintenance of the murine embryonic stem cell phenotype.Stem Cells. 2009 Aug;27(8):1782-91. doi: 10.1002/stem.97. Stem Cells. 2009. PMID: 19544432
-
EpCAM cellular functions in adhesion and migration, and potential impact on invasion: A critical review.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020 Dec;1874(2):188436. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188436. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32976980 Review.
-
Epithelial cell adhesion molecule expression (CD326) in cancer: a short review.Cancer Treat Rev. 2012 Feb;38(1):68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2011.04.002. Epub 2011 May 14. Cancer Treat Rev. 2012. PMID: 21576002 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of the Function and Expression of EpCAM.Biomedicines. 2024 May 20;12(5):1129. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12051129. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38791091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EpCAM overexpression prolongs proliferative capacity of primary human breast epithelial cells and supports hyperplastic growth.Mol Cancer. 2013 Jun 10;12:56. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-56. Mol Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23758908 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of EpCAM in physiological processes and diseases (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2018 Oct;42(4):1771-1785. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3764. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30015855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ping-Pong-Tumor and Host in Pancreatic Cancer Progression.Front Oncol. 2019 Dec 16;9:1359. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01359. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31921628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatiotemporal patterning of EpCAM is important for murine embryonic endo- and mesodermal differentiation.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 29;8(1):1801. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20131-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29379062 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cirulli V., Crisa L., Beattie G.M., Mally M.I., Lopez A.D., Fannon A., Ptasznik A., Inverardi L., Ricordi C., Deerinck T., et al. 1998. KSA antigen Ep-CAM mediates cell-cell adhesion of pancreatic epithelial cells: morphoregulatory roles in pancreatic islet development. J. Cell Biol. 140:1519–1534 10.1083/jcb.140.6.1519 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

