Eosinophil cysteinyl leukotriene synthesis mediated by exogenous secreted phospholipase A2 group X
- PMID: 20974857
- PMCID: PMC3009875
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.153338
Eosinophil cysteinyl leukotriene synthesis mediated by exogenous secreted phospholipase A2 group X
Abstract
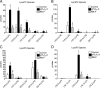
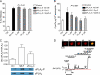
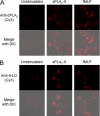
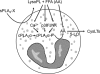
Secreted phospholipase A(2) group X (sPLA(2)-X) has recently been identified in the airways of patients with asthma and may participate in cysteinyl leukotriene (CysLT; C(4), D(4), and E(4)) synthesis. We examined CysLT synthesis and arachidonic acid (AA) and lysophospholipid release by eosinophils mediated by recombinant human sPLA(2)-X. We found that recombinant sPLA(2)-X caused marked AA release and a rapid onset of CysLT synthesis in human eosinophils that was blocked by a selective sPLA(2)-X inhibitor. Exogenous sPLA(2)-X released lysophospholipid species that arise from phospholipids enriched in AA in eosinophils, including phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylinositol, and phosphatidylethanolamine as well as plasmenyl phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine. CysLT synthesis mediated by sPLA(2)-X but not AA release could be suppressed by inhibition of cPLA(2)α. Exogenous sPLA(2)-X initiated Ser(505) phosphorylation of cPLA(2)α, an intracellular Ca(2+) flux, and translocation of cPLA(2)α and 5-lipoxygenase in eosinophils. Synthesis of CysLTs in response to sPLA(2)-X or lysophosphatidylcholine was inhibited by p38 or JNK inhibitors but not by a MEK 1/2 inhibitor. A further increase in CysLT synthesis was induced by the addition of sPLA(2)-X to eosinophils under conditions of N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-mediated cPLA(2)α activation. These results indicate that sPLA(2)-X participates in AA and lysophospholipid release, resulting in CysLT synthesis in eosinophils through a mechanism involving p38 and JNK MAPK, cPLA(2)α, and 5-lipoxygenase activation and resulting in the amplification of CysLT synthesis during cPLA(2)α activation. Transactivation of eosinophils by sPLA(2)-X may be an important mechanism leading to CysLT formation in the airways of patients with asthma.
Figures
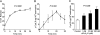
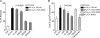
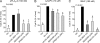
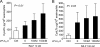
References
-
- Pavord I. D., Ward R., Woltmann G., Wardlaw A. J., Sheller J. R., Dworski R. (1999) Am. J. Respir Crit. Care Med. 160, 1905–1909 - PubMed
-
- Romagnoli M., Vachier I., Tarodo de la Fuente P., Meziane H., Chavis C., Bousquet J., Godard P., Chanez P. (2002) Eur. Respir. J. 20, 1370–1377 - PubMed
-
- Ago H., Kanaoka Y., Irikura D., Lam B. K., Shimamura T., Austen K. F., Miyano M. (2007) Nature 448, 609–612 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

