pex5 Mutants that differentially disrupt PTS1 and PTS2 peroxisomal matrix protein import in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 20974890
- PMCID: PMC2996013
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.110.162479
pex5 Mutants that differentially disrupt PTS1 and PTS2 peroxisomal matrix protein import in Arabidopsis
Abstract
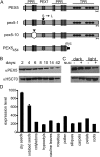
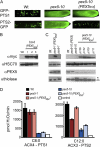
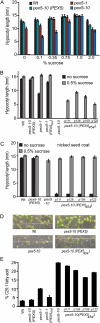
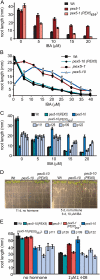
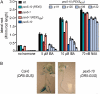
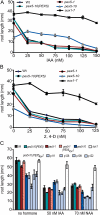
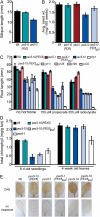
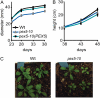
PEX5 and PEX7 are receptors required for the import of peroxisome-bound proteins containing one of two peroxisomal targeting signals (PTS1 or PTS2). To better understand the role of PEX5 in plant peroxisomal import, we characterized the Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) pex5-10 mutant, which has a T-DNA insertion in exon 5 of the PEX5 gene. Sequencing results revealed that exon 5, along with the T-DNA, is removed in this mutant, resulting in a truncated pex5 protein. The pex5-10 mutant has germination defects and is completely dependent on exogenous Suc for early seedling establishment, based on poor utilization of seed-storage fatty acids. This mutant also has delayed development and reduced fertility, although adult pex5-10 plants appear normal. Peroxisomal metabolism of indole-3-butyric acid, propionate, and isobutyrate also is disrupted. The pex5-10 mutant has reduced import of both PTS1 and PTS2 proteins, and enzymatic processes that occur in peroxisomes are disrupted. To specifically study the import and importance of PTS1 proteins, we made a truncated PEX5 construct lacking the PTS1-binding region (PEX5(454)). Transformation of this construct into pex5-10 resulted in the rescue of PTS2 import, thereby creating a line with PTS1-specific import defects. The pex5-10 (PEX5(454)) plants still had developmental defects, although restoring PTS2 import resulted in a less severe mutant phenotype. Comparison of pex5-10 and pex5-10 (PEX5(454)) phenotypes can separate the import mechanisms for enzymes acting in different peroxisomal processes, including indole-3-butyric acid/2,4-dichlorophenoxybutyric acid oxidation, isobutyrate and propionate metabolism, and photorespiration.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Peroxisomal ubiquitin-protein ligases peroxin2 and peroxin10 have distinct but synergistic roles in matrix protein import and peroxin5 retrotranslocation in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2014 Nov;166(3):1329-44. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.247148. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Plant Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25214533 Free PMC article.
-
The Arabidopsis peroxisomal targeting signal type 2 receptor PEX7 is necessary for peroxisome function and dependent on PEX5.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Feb;16(2):573-83. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-05-0422. Epub 2004 Nov 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15548601 Free PMC article.
-
Interdependence of the peroxisome-targeting receptors in Arabidopsis thaliana: PEX7 facilitates PEX5 accumulation and import of PTS1 cargo into peroxisomes.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Apr 1;21(7):1263-71. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-08-0672. Epub 2010 Feb 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20130089 Free PMC article.
-
Structural biology of the import pathways of peroxisomal matrix proteins.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 May;1863(5):804-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.09.034. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26450166 Review.
-
Characterization, prediction and evolution of plant peroxisomal targeting signals type 1 (PTS1s).Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 May;1863(5):790-803. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.01.001. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26772785 Review.
Cited by
-
Peroxisomal ubiquitin-protein ligases peroxin2 and peroxin10 have distinct but synergistic roles in matrix protein import and peroxin5 retrotranslocation in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2014 Nov;166(3):1329-44. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.247148. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Plant Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25214533 Free PMC article.
-
Plant peroxisomes: recent discoveries in functional complexity, organelle homeostasis, and morphological dynamics.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2016 Dec;34:17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2016.07.008. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2016. PMID: 27500947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crystal structure of peroxisomal targeting signal-2 bound to its receptor complex Pex7p-Pex21p.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013 Aug;20(8):987-93. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2618. Epub 2013 Jun 30. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23812376
-
The Early-Acting Peroxin PEX19 Is Redundantly Encoded, Farnesylated, and Essential for Viability in Arabidopsis thaliana.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 29;11(1):e0148335. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148335. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26824478 Free PMC article.
-
Covalent Label Transfer between Peroxisomal Importomer Components Reveals Export-driven Import Interactions.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jan 29;291(5):2460-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.686501. Epub 2015 Nov 13. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26567336 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adham AR, Zolman BK, Millius A, Bartel B. (2005) Mutations in Arabidopsis acyl-CoA oxidase genes reveal distinct and overlapping roles in β-oxidation. Plant J 41: 859–874 - PubMed
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al. (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Clough SJ, Bent AF. (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana Plant J 16: 735–743 - PubMed
-
- Costa-Rodrigues J, Carvalho AF, Gouveia AM, Fransen M, Sá-Miranda C, Azevedo JE. (2004) The N terminus of the peroxisomal cycling receptor, Pex5p, is required for redirecting the peroxisome-associated peroxin back to the cytosol. J Biol Chem 279: 46573–46579 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

