Cytokine-dependent but acquired immunity-independent arthritis caused by DNA escaped from degradation
- PMID: 20974942
- PMCID: PMC2984163
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1010603107
Cytokine-dependent but acquired immunity-independent arthritis caused by DNA escaped from degradation
Abstract
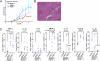
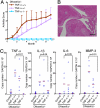
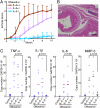
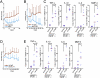
DNase II digests the chromosomal DNA in macrophages after apoptotic cells and nuclei from erythroid precursors are engulfed. The DNase II-null mice develop a polyarthritis that resembles rheumatoid arthritis. Here, we showed that when bone marrow cells from the DNase II-deficient mice were transferred to the wild-type mice, they developed arthritis. A deficiency of Rag2 or a lack of lymphocytes accelerated arthritis of the DNase II-null mice, suggesting that the DNase II(-/-) macrophages were responsible for triggering arthritis, and their lymphocytes worked protectively. A high level of TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6 was found in the affected joints of the DNase II-null mice, suggesting an inflammatory-skewed cytokine storm was established in the joints. A lack of TNFα, IL-1β, or IL-6 gene blocked the expression of the other cytokine genes as well and inhibited the development of arthritis. Neutralization of TNFα, IL-1β, or IL-6 had a therapeutic effect on the developed arthritis of the DNase II-null mice, indicating that the cytokine storm was essential for the maintenance of arthritis in the DNase II-deficient mice. Methotrexate, an antimetabolite that is often used to treat patients with rheumatoid arthritis, had a therapeutic effect with the DNase II-null mice. These properties of arthritis in the DNase II-null mice were similar to those found in human systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis or Still's disease, indicating that the DNase II-null mice are a good animal model of this type of arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423:356–361. - PubMed
-
- Tedder TF. CD19: A promising B cell target for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009;5:572–577. - PubMed
-
- Feldmann M, Maini SR. Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis: An education in pathophysiology and therapeutics. Immunol Rev. 2008;223:7–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

