Epithelial reticulon 4B (Nogo-B) is an endogenous regulator of Th2-driven lung inflammation
- PMID: 20975041
- PMCID: PMC2989775
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20100786
Epithelial reticulon 4B (Nogo-B) is an endogenous regulator of Th2-driven lung inflammation
Abstract
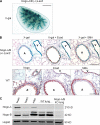
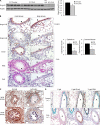
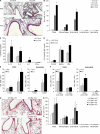
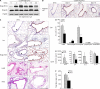
Nogo-B is a member of the reticulon family of proteins (RTN-4B) that is highly expressed in lung tissue; however, its function remains unknown. We show that mice with Th2-driven lung inflammation results in a loss of Nogo expression in airway epithelium and smooth muscle compared with nonallergic mice, a finding which is replicated in severe human asthma. Mice lacking Nogo-A/B (Nogo-KO) display an exaggerated asthma-like phenotype, and epithelial reconstitution of Nogo-B in transgenic mice blunts Th2-mediated lung inflammation. Microarray analysis of lungs from Nogo-KO mice reveals a marked reduction in palate lung and nasal clone (PLUNC) gene expression, and the levels of PLUNC are enhanced in epithelial Nogo-B transgenic mice. Finally, transgenic expression of PLUNC into Nogo-KO mice rescues the enhanced asthmatic-like responsiveness in these KO mice. These data identify Nogo-B as a novel protective gene expressed in lung epithelia, and its expression regulates the levels of the antibacterial antiinflammatory protein PLUNC.
Figures

References
-
- Chu H.W., Thaikoottathil J., Rino J.G., Zhang G., Wu Q., Moss T., Refaeli Y., Bowler R., Wenzel S.E., Chen Z., et al. 2007. Function and regulation of SPLUNC1 protein in Mycoplasma infection and allergic inflammation. J. Immunol. 179:3995–4002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

