Glycogen storage disease type I and G6Pase-β deficiency: etiology and therapy
- PMID: 20975743
- PMCID: PMC4178929
- DOI: 10.1038/nrendo.2010.189
Glycogen storage disease type I and G6Pase-β deficiency: etiology and therapy
Abstract
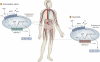
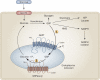
Glycogen storage disease type I (GSD-I) consists of two subtypes: GSD-Ia, a deficiency in glucose-6-phosphatase-α (G6Pase-α) and GSD-Ib, which is characterized by an absence of a glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) transporter (G6PT). A third disorder, G6Pase-β deficiency, shares similarities with this group of diseases. G6Pase-α and G6Pase-β are G6P hydrolases in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum, which depend on G6PT to transport G6P from the cytoplasm into the lumen. A functional complex of G6PT and G6Pase-α maintains interprandial glucose homeostasis, whereas G6PT and G6Pase-β act in conjunction to maintain neutrophil function and homeostasis. Patients with GSD-Ia and those with GSD-Ib exhibit a common metabolic phenotype of disturbed glucose homeostasis that is not evident in patients with G6Pase-β deficiency. Patients with a deficiency in G6PT and those lacking G6Pase-β display a common myeloid phenotype that is not shared by patients with GSD-Ia. Previous studies have shown that neutrophils express the complex of G6PT and G6Pase-β to produce endogenous glucose. Inactivation of either G6PT or G6Pase-β increases neutrophil apoptosis, which underlies, at least in part, neutrophil loss (neutropenia) and dysfunction in GSD-Ib and G6Pase-β deficiency. Dietary and/or granulocyte colony-stimulating factor therapies are available; however, many aspects of the diseases are still poorly understood. This Review will address the etiology of GSD-Ia, GSD-Ib and G6Pase-β deficiency and highlight advances in diagnosis and new treatment approaches, including gene therapy.
Figures

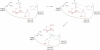
References
-
- Chou JY, Matern D, Mansfield BC, Chen YT. Type I glycogen storage diseases: disorders of the glucose-6-phosphatase complex. Curr. Mol. Med. 2002;2:121–143. - PubMed
-
- Chou JY, Mansfield BC. In: Membrane Transporter Diseases. Broer S, Wagner CA, editors. Springer; New York: 2003. pp. 191–205. Ch. 13.
-
- Lei K-J, Shelly LL, Pan C-J, Sidbury JB, Chou JY. Mutations in the glucose-6-phosphatase gene that cause glycogen storage disease type 1a. Science. 1993;262:580–583. - PubMed
-
- Hiraiwa H, Pan C-J, Lin B, Moses SW, Chou JY. Inactivation of the glucose 6-phosphate transporter causes glycogen storage disease type 1b. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:5532–5536. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

