Epigenetic choreographers of neurogenesis in the adult mammalian brain
- PMID: 20975758
- PMCID: PMC3324277
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2672
Epigenetic choreographers of neurogenesis in the adult mammalian brain
Abstract
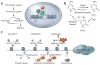
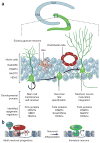
Epigenetic mechanisms regulate cell differentiation during embryonic development and also serve as important interfaces between genes and the environment in adulthood. Neurogenesis in adults, which generates functional neural cell types from adult neural stem cells, is dynamically regulated by both intrinsic state-specific cell differentiation cues and extrinsic neural niche signals. Epigenetic regulation by DNA and histone modifiers, non-coding RNAs and other self-sustained mechanisms can lead to relatively long-lasting biological effects and maintain functional neurogenesis throughout life in discrete regions of the mammalian brain. Here, we review recent evidence that epigenetic mechanisms carry out diverse roles in regulating specific aspects of adult neurogenesis and highlight the implications of such epigenetic regulation for neural plasticity and disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Cameron HA, McKay RD. Adult neurogenesis produces a large pool of new granule cells in the dentate gyrus. J Comp Neurol. 2001;435:406–417. - PubMed
-
- Altman J, Das GD. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol. 1965;124:319–335. - PubMed
-
- Gage FH. Mammalian neural stem cells. Science. 2000;287:1433–1438. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Buylla A, Lim DA. For the long run: maintaining germinal niches in the adult brain. Neuron. 2004;41:683–686. - PubMed
-
- Ming GL, Song H. Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2005;28:223–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HD069184/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG024984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MH090258/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS047344/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MH087874/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS047344/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS048271/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS047344/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH088485/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090258/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH087874/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AG024984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R33 MH087874/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NS048271/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MH088485/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HD069184/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- NS047344/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

