Recognizing independent and joint activities among multiple residents in smart environments
- PMID: 20975986
- PMCID: PMC2958106
- DOI: 10.1007/s12652-009-0007-1
Recognizing independent and joint activities among multiple residents in smart environments
Abstract
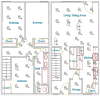
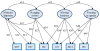
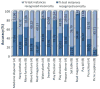
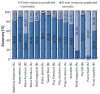
The pervasive sensing technologies found in smart homes offer unprecedented opportunities for providing health monitoring and assistance to individuals experiencing difficulties living independently at home. A primary challenge that needs to be tackled to meet this need is the ability to recognize and track functional activities that people perform in their own homes and everyday settings. In this paper, we look at approaches to perform real-time recognition of Activities of Daily Living. We enhance other related research efforts to develop approaches that are effective when activities are interrupted and interleaved. To evaluate the accuracy of our recognition algorithms we assess them using real data collected from participants performing activities in our on-campus smart apartment testbed.
Figures

References
-
- Cook DJ, Das SK, editors. Smart environments: technology, protocols, and applications. 1st. Wiley; New York: 2004.
-
- Doctor F, Hagras H, Callaghan V. A fuzzy embedded agent-based approach for realizing ambient intelligence in intelligent inhabited environments. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part A. 2005;35(1):55–56.
-
- Liao L, Fox D, Kautz H. Location-based activity recognition using relational Markov networks. Proceedings of the international joint conference on artificial intelligence; 2005. pp. 773–778.
-
- Maurer U, Smailagic A, Siewiorek D, Deisher M. Activity recognition and monitoring using multiple sensors on different body positions. Proceedings of the international workshop on wearable and implantable body sensor networks; 2006. pp. 113–116.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
