Automatic versus voluntary motor imitation: effect of visual context and stimulus velocity
- PMID: 20976006
- PMCID: PMC2958128
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013506
Automatic versus voluntary motor imitation: effect of visual context and stimulus velocity
Abstract
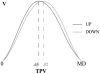
Automatic imitation is the tendency to reproduce observed actions involuntarily. Though this topic has been widely treated, at present little is known about the automatic imitation of the kinematic features of an observed movement. The present study was designed to understand if the kinematics of a previously seen stimulus primes the executed action, and if this effect is sensitive to the kinds of stimuli presented. We proposed a simple imitation paradigm in which a dot or a human demonstrator moved in front of the participant who was instructed either to reach the final position of the stimulus or to imitate its motion with his or her right arm. Participants' movements were automatically contaminated by stimulus velocity when it moved according to biological laws, suggesting that automatic imitation was kinematic dependent. Despite that the performance, in term of reproduced velocity, improved in a context of voluntary imitation, subjects did not replicate the observed motions exactly. These effects were not affected by the kind of stimuli used, i.e., motor responses were influenced in the same manner after dot or human observation. These findings support the existence of low-level sensory-motor matching mechanisms that work on movement planning and represent the basis for higher levels of social interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Meltzoff AN, Moore MK. Imitation of Facial and Manual Gestures by Human Neonates. Science. 1977;198:75–78. - PubMed
-
- Chartrand TL, Bargh JA. The chameleon effect: the perception-behavior link and social interaction. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1999;76:893–910. - PubMed
-
- Byrne RW, Russon AE. Learning by imitation: a hierarchical approach. Behav Brain Sci. 1998;21:667–84; discussion 684–721. - PubMed
-
- Rizzolatti G, Fogassi L, Gallese V. Neurophysiological mechanisms underlying the understanding and imitation of action. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:661–670. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

