The microRNA and messengerRNA profile of the RNA-induced silencing complex in human primary astrocyte and astrocytoma cells
- PMID: 20976148
- PMCID: PMC2956662
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013445
The microRNA and messengerRNA profile of the RNA-induced silencing complex in human primary astrocyte and astrocytoma cells
Abstract
Background: GW/P bodies are cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein-rich foci involved in microRNA (miRNA)-mediated messenger RNA (mRNA) silencing and degradation. The mRNA regulatory functions within GW/P bodies are mediated by GW182 and its binding partner hAgo2 that bind miRNA in the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). To date there are no published reports of the profile of miRNA and mRNA targeted to the RISC or a comparison of the RISC-specific miRNA/mRNA profile differences in malignant and non-malignant cells.
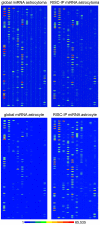
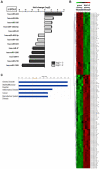
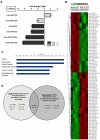
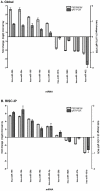
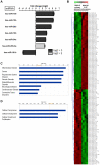
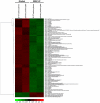
Methodology/principal findings: RISC mRNA and miRNA components were profiled by microarray analysis of malignant human U-87 astrocytoma cells and its non-malignant counterpart, primary human astrocytes. Total cell RNA as well as RNA from immunoprecipitated RISC was analyzed. The novel findings were fourfold: (1) miRNAs were highly enriched in astrocyte RISC compared to U-87 astrocytoma RISC, (2) astrocytoma and primary astrocyte cells each contained unique RISC miRNA profiles as compared to their respective cellular miRNA profiles, (3) miR-195, 10b, 29b, 19b, 34a and 455-3p levels were increased and the miR-181b level was decreased in U-87 astrocytoma RISC as compared to astrocyte RISC, and (4) the RISC contained decreased levels of mRNAs in primary astrocyte and U-87 astrocytoma cells.
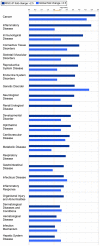
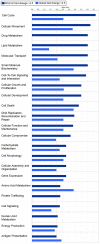
Conclusions/significance: The observation that miR-34a and miR-195 levels were increased in the RISC of U-87 astrocytoma cells suggests an oncogenic role for these miRNAs. Differential regulation of mRNAs by specific miRNAs is evidenced by the observation that three miR34a-targeted mRNAs and two miR-195-targeted mRNAs were downregulated while one miR-195-targeted mRNA was upregulated. Biological pathway analysis of RISC mRNA components suggests that the RISC plays a pivotal role in malignancy and other conditions. This study points to the importance of the RISC and ultimately GW/P body composition and function in miRNA and mRNA deregulation in astrocytoma cells and possibly in other malignancies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
RIP-Chip analysis supports different roles for AGO2 and GW182 proteins in recruiting and processing microRNA targets.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Apr 18;20(Suppl 4):120. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2683-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30999843 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the miRNA-mRNA-lncRNA networks in ER+ and ER- breast cancer cell lines.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 Dec;19(12):2874-87. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12681. Epub 2015 Sep 28. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26416600 Free PMC article.
-
DDX6 post-transcriptionally down-regulates miR-143/145 expression through host gene NCR143/145 in cancer cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1829(10):1102-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.07.010. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23932921
-
The Non-Canonical Aspects of MicroRNAs: Many Roads to Gene Regulation.Cells. 2019 Nov 19;8(11):1465. doi: 10.3390/cells8111465. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31752361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular and extracellular microRNA: An update on localization and biological role.Prog Histochem Cytochem. 2016 Nov;51(3-4):33-49. doi: 10.1016/j.proghi.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jun 25. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 2016. PMID: 27396686 Review.
Cited by
-
Control by a hair's breadth: the role of microRNAs in the skin.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Apr;70(7):1149-69. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1117-z. Epub 2012 Sep 15. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 22983383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory RNAs and control of epigenetic mechanisms: expectations for cognition and cognitive dysfunction.Epigenomics. 2016 Jan;8(1):135-51. doi: 10.2217/epi.15.79. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Epigenomics. 2016. PMID: 26366811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-103/miR-195/miR-15b Regulate SALL4 and Inhibit Proliferation and Migration in Glioma.Molecules. 2018 Nov 10;23(11):2938. doi: 10.3390/molecules23112938. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30423818 Free PMC article.
-
Haptoglobin modulates beta-amyloid uptake by U-87 MG astrocyte cell line.J Mol Neurosci. 2015 May;56(1):35-47. doi: 10.1007/s12031-014-0465-6. Epub 2014 Nov 18. J Mol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25403907
-
MicroRNA-based regulation of Aurora A kinase in breast cancer.Oncotarget. 2020 Nov 17;11(46):4306-4324. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27811. eCollection 2020 Nov 17. Oncotarget. 2020. PMID: 33245732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mello CC, Conte D., Jr Revealing the world of RNA interference. Nature. 2004;431:338–342. - PubMed
-
- Meister G, Tuschl T. Mechanisms of gene silencing by double-stranded RNA. Nature. 2004;431:343–349. - PubMed
-
- Jakymiw A, Pauley KM, Li S, Ikeda K, Lian S, et al. The role of GW/P bodies in RNA processing and silencing. J Cell Sci. 2007;120:1317–1323. - PubMed
-
- Eulalio A, Behm-Ansmant I, Izaurralde E. P bodies: at the crossroads of post-transcriptional pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:9–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

