Hypercholesterolemia impaired sperm functionality in rabbits
- PMID: 20976152
- PMCID: PMC2956674
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013457
Hypercholesterolemia impaired sperm functionality in rabbits
Abstract
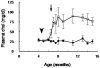
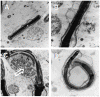
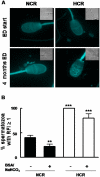
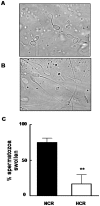
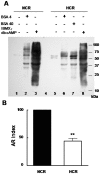
Hypercholesterolemia represents a high risk factor for frequent diseases and it has also been associated with poor semen quality that may lead to male infertility. The aim of this study was to analyze semen and sperm function in diet-induced hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Twelve adult White New Zealand male rabbits were fed ad libitum a control diet or a diet supplemented with 0.05% cholesterol. Rabbits under cholesterol-enriched diet significantly increased total cholesterol level in the serum. Semen examination revealed a significant reduction in semen volume and sperm motility in hypercholesterolemic rabbits (HCR). Sperm cell morphology was seriously affected, displaying primarily a "folded head"-head fold along the major axe-, and the presence of cytoplasmic droplet on sperm flagellum. Cholesterol was particularly increased in acrosomal region when detected by filipin probe. The rise in cholesterol concentration in sperm cells was determined quantitatively by Gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analyses. We also found a reduction of protein tyrosine phosphorylation in sperm incubated under capacitating conditions from HCR. Interestingly, the addition of Protein Kinase A pathway activators -dibutyryl-cyclic AMP and iso-butylmethylxanthine- to the medium restored sperm capacitation. Finally, it was also reported a significant decrease in the percentage of reacted sperm in the presence of progesterone. In conclusion, our data showed that diet-induced hypercholesterolemia adversely affects semen quality and sperm motility, capacitation and acrosomal reaction in rabbits; probably due to an increase in cellular cholesterol content that alters membrane related events.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kannel WB, Castelli WP, Gordon T. Cholesterol in the prediction of atherosclerotic disease: new perspectives based on the Framingham Study. Ann Intern Med. 1979;90:85–91. - PubMed
-
- Yeagle PL. Cholesterol and the cell membrane. Biochim. Biophys Acta. 1985;9;822(3–4):267–87. - PubMed
-
- Visconti PE, Ning X, Fornes MW, Alvarez JG, Stein P, et al. Cholesterol efflux-mediated signal transduction in mammalian sperm: cholesterol release signals an increase in protein tyrosine phosphorylation during mouse sperm capacitation. Dev Biol. 1999b;214(2):429–43. - PubMed
-
- Eyster KM. The membrane and lipids as integral participants in signal transduction: lipid signal transduction for the non-lipid biochemist. Adv Physiol Educ. 2007;31:5–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

