Deficiency of activating Fcγ-receptors reduces hepatic clearance and deposition of IC and increases CIC levels in mercury-induced autoimmunity
- PMID: 20976163
- PMCID: PMC2955531
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013413
Deficiency of activating Fcγ-receptors reduces hepatic clearance and deposition of IC and increases CIC levels in mercury-induced autoimmunity
Abstract
Background: Inorganic mercury (Hg) induces a T-cell dependent, systemic autoimmune condition (HgIA) where activating Fcγ-receptors (FcγRs) are important for the induction. In this study we examined the influence of activating FcγRs on circulating levels and organ localization of immune complexes (IC) in HgIA.
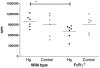
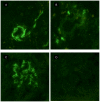
Methods and principal findings: Mercury treated BALB/c wt mice showed a significant but modest increase of circulating IC (CIC) from day 12 until day 18 and day 35 for IgG2a- and IgG1- CIC, respectively. Mercury-treated mice lacking the trans-membrane γ-chain of activating FcγRs (FcRγ(-/-)) had significantly higher CIC levels of both IgG1-CIC and IgG2a-CIC than wt mice during the treatment course. The hepatic uptake of preformed CIC was significantly more efficient in wt mice compared to FcγR(-/-) mice, but also development of extrahepatic tissue IC deposits was delayed in FcRγ(-/-) mice. After 35 days of Hg treatment the proportion of immune deposits, as well as the amounts was significantly reduced in vessel FcRγ(-/-) mice compared to wt mice.
Conclusions: We conclude that mice lacking functional activating FcγRs respond to Hg with increased levels and altered quality of CIC compared with wt mice. Lack of functional activating FcγRs delayed the elimination of CIC, but also significantly reduced extrahepatic tissue localization of CIC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of Fc-receptors in murine mercury-induced systemic autoimmunity.Clin Exp Immunol. 2006 May;144(2):309-18. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03057.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16634805 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of activating and inhibiting Fc-receptors on murine mercury-induced autoimmunity.J Autoimmun. 2008 Aug;31(1):22-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2008.01.002. Epub 2008 Mar 7. J Autoimmun. 2008. PMID: 18314309
-
FcRγ-chain ITAM signaling is critically required for cross-presentation of soluble antibody-antigen complexes by dendritic cells.J Immunol. 2014 Dec 1;193(11):5506-14. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302012. Epub 2014 Oct 29. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25355925
-
Low-affinity Fcgamma receptors, autoimmunity and infection.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2009 Aug 13;11:e24. doi: 10.1017/S1462399409001161. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19674504 Review.
-
Organic mercury compounds and autoimmunity.Autoimmun Rev. 2005 Jun;4(5):270-5. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2004.12.001. Epub 2005 Jan 5. Autoimmun Rev. 2005. PMID: 15990073 Review.
Cited by
-
The Potential Roles of Bisphenol A (BPA) Pathogenesis in Autoimmunity.Autoimmune Dis. 2014;2014:743616. doi: 10.1155/2014/743616. Epub 2014 Apr 7. Autoimmune Dis. 2014. PMID: 24804084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lupus-like oral mucosal lesions in mercury-induced autoimmune response in Brown Norway rats.BMC Immunol. 2013 Oct 3;14:47. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-14-47. BMC Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24089704 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nangaku M, Couser WG. Mechanisms of immune-deposit formation and the mediation of immune renal injury. Clinical and experimental nephrology. 2005;9:183–191. - PubMed
-
- Heyman B. Feedback regulation by IgG antibodies. Immunology letters. 2003;88:157–161. - PubMed
-
- Ravetch J. In vivo veritas: the surprising roles of Fc receptors in immunity. Nature immunology. 11:183–185. - PubMed
-
- Johansson AG, Lovdal T, Magnusson KE, Berg T, Skogh T. Liver cell uptake and degradation of soluble immunoglobulin G immune complexes in vivo and in vitro in rats. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md. 1996;24:169–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

