Transcriptome analysis revealed unique genes as targets for the anti-inflammatory action of activated protein C in human macrophages
- PMID: 20976180
- PMCID: PMC2955553
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015352
Transcriptome analysis revealed unique genes as targets for the anti-inflammatory action of activated protein C in human macrophages
Abstract
Background: Activated protein C (APC) has been introduced as a therapeutic agent for treatment of patients with severe sepsis due to its unique anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory properties in the vascular system. In this study we investigated novel targets for the anti-inflammatory action of APC in human macrophages.
Methods: Using a genome-wide approach, effects of APC on the expression profile in inflammatory activated human macrophages were analyzed.
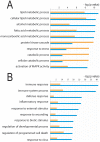
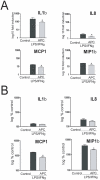
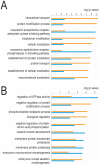
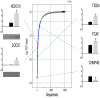
Results: We identified, for the first time, genes that are specifically regulated by APC under inflammatory conditions, such as chromatin binding protein 4B (CHMP4B) and p300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF), thus indicating a role of APC in the epigenetic control of gene transcription. A functional assay showed the influence of APC in the acetyltransferase/deacetylase activity of nuclear extracts from inflamed macrophages.
Conclusion: Our data sheds new light on APC targets in inflammation and opens new lines of investigation that may be explored in order to further elucidate its unique molecule properties.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wnt5A/CaMKII signaling contributes to the inflammatory response of macrophages and is a target for the antiinflammatory action of activated protein C and interleukin-10.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008 Mar;28(3):504-10. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.157438. Epub 2008 Jan 3. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008. PMID: 18174455
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of allylpyrocatechol in LPS-induced macrophages is mediated by suppression of iNOS and COX-2 via the NF-kappaB pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2008 Sep;8(9):1264-71. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2008.05.003. Epub 2008 Jun 6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18602073
-
Gene expression profiling of inflamed human endothelial cells and influence of activated protein C.Circulation. 2004 Nov 2;110(18):2903-9. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000146344.49689.BB. Epub 2004 Oct 25. Circulation. 2004. PMID: 15505101
-
Protective mechanisms of activated protein C in severe inflammatory disorders.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Oct;158(4):1034-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00251.x. Epub 2009 May 14. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19466992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein C anticoagulant pathway and its role in controlling microvascular thrombosis and inflammation.Crit Care Med. 2001 Jul;29(7 Suppl):S48-51; discussion 51-2. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200107001-00018. Crit Care Med. 2001. PMID: 11445734 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-4 Causes Hyperpermeability of Vascular Endothelial Cells through Wnt5A Signaling.PLoS One. 2016 May 23;11(5):e0156002. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156002. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27214384 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of endogenous activated protein C attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inducing myeloid-derived suppressor cells.J Immunol. 2013 Oct 1;191(7):3764-77. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202556. Epub 2013 Aug 30. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23997223 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of p300/CBP-Associated Factor Attenuates Renal Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis through Modulation of NF-kB and Nrf2.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 28;20(7):1554. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071554. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30925687 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships Among Circulating Levels of Hemostasis Inhibitors, Chemokines, Adhesion Molecules, and MRI Characteristics in Multiple Sclerosis.Front Neurol. 2020 Oct 15;11:553616. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.553616. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33178104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Charo IF, Ransohoff RM. The Many Roles of Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors in Inflammation. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:610–621. - PubMed
-
- Cohen J. The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature. 2002;420:885–891. - PubMed
-
- Bernard GR, Vincent J-L, Laterre P-F, LaRosa SP, Dhainaut J-F, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Recombinant Human Activated Protein C for Severe Sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:699–709. - PubMed
-
- Cavaillon JM A-CM. Monocytes/macrophages and sepsis. Critical Care Medicine. 2005;33:S506–S509. - PubMed
-
- Toltl L, Swystun LL, Pepler L, Liaw P. Protective effects of activated protein C in sepsis. Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 2008;100:582–592. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

