A novel adaptive method for the analysis of next-generation sequencing data to detect complex trait associations with rare variants due to gene main effects and interactions
- PMID: 20976247
- PMCID: PMC2954824
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001156
A novel adaptive method for the analysis of next-generation sequencing data to detect complex trait associations with rare variants due to gene main effects and interactions
Abstract
There is solid evidence that rare variants contribute to complex disease etiology. Next-generation sequencing technologies make it possible to uncover rare variants within candidate genes, exomes, and genomes. Working in a novel framework, the kernel-based adaptive cluster (KBAC) was developed to perform powerful gene/locus based rare variant association testing. The KBAC combines variant classification and association testing in a coherent framework. Covariates can also be incorporated in the analysis to control for potential confounders including age, sex, and population substructure. To evaluate the power of KBAC: 1) variant data was simulated using rigorous population genetic models for both Europeans and Africans, with parameters estimated from sequence data, and 2) phenotypes were generated using models motivated by complex diseases including breast cancer and Hirschsprung's disease. It is demonstrated that the KBAC has superior power compared to other rare variant analysis methods, such as the combined multivariate and collapsing and weight sum statistic. In the presence of variant misclassification and gene interaction, association testing using KBAC is particularly advantageous. The KBAC method was also applied to test for associations, using sequence data from the Dallas Heart Study, between energy metabolism traits and rare variants in ANGPTL 3,4,5 and 6 genes. A number of novel associations were identified, including the associations of high density lipoprotein and very low density lipoprotein with ANGPTL4. The KBAC method is implemented in a user-friendly R package.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

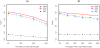
 using 2,000 replicates for each scenario.
using 2,000 replicates for each scenario.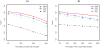
 using 2,000 replicates for each scenario.
using 2,000 replicates for each scenario.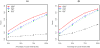
 using 2,000 replicates.
using 2,000 replicates.Similar articles
-
A fast and noise-resilient approach to detect rare-variant associations with deep sequencing data for complex disorders.Genet Epidemiol. 2012 Nov;36(7):675-85. doi: 10.1002/gepi.21662. Epub 2012 Aug 3. Genet Epidemiol. 2012. PMID: 22865616 Free PMC article.
-
Association studies for next-generation sequencing.Genome Res. 2011 Jul;21(7):1099-108. doi: 10.1101/gr.115998.110. Epub 2011 Apr 26. Genome Res. 2011. PMID: 21521787 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive ridge regression for rare variant detection.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e44173. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044173. Epub 2012 Aug 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22952918 Free PMC article.
-
A generalized genetic random field method for the genetic association analysis of sequencing data.Genet Epidemiol. 2014 Apr;38(3):242-53. doi: 10.1002/gepi.21790. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Genet Epidemiol. 2014. PMID: 24482034 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical analysis of rare sequence variants: an overview of collapsing methods.Genet Epidemiol. 2011;35 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S12-7. doi: 10.1002/gepi.20643. Genet Epidemiol. 2011. PMID: 22128052 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The power of gene-based rare variant methods to detect disease-associated variation and test hypotheses about complex disease.PLoS Genet. 2015 Apr 23;11(4):e1005165. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005165. eCollection 2015 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25906071 Free PMC article.
-
Scan-statistic approach identifies clusters of rare disease variants in LRP2, a gene linked and associated with autism spectrum disorders, in three datasets.Am J Hum Genet. 2012 Jun 8;90(6):1002-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.04.010. Epub 2012 May 10. Am J Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 22578327 Free PMC article.
-
Haplotype kernel association test as a powerful method to identify chromosomal regions harboring uncommon causal variants.Genet Epidemiol. 2013 Sep;37(6):560-70. doi: 10.1002/gepi.21740. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Genet Epidemiol. 2013. PMID: 23740760 Free PMC article.
-
Rare genetic variants and treatment response: sample size and analysis issues.Stat Med. 2012 Nov 10;31(25):3041-50. doi: 10.1002/sim.5428. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Stat Med. 2012. PMID: 22736504 Free PMC article.
-
Utilising family-based designs for detecting rare variant disease associations.Ann Hum Genet. 2014 Mar;78(2):129-40. doi: 10.1111/ahg.12051. Ann Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24571231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen JC, Kiss RS, Pertsemlidis A, Marcel YL, McPherson R, et al. Multiple rare alleles contribute to low plasma levels of HDL cholesterol. Science. 2004;305:869–872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

