Error-Prone Translesion DNA Synthesis by Escherichia coli DNA Polymerase IV (DinB) on Templates Containing 1,2-dihydro-2-oxoadenine
- PMID: 20976264
- PMCID: PMC2952919
- DOI: 10.4061/2010/807579
Error-Prone Translesion DNA Synthesis by Escherichia coli DNA Polymerase IV (DinB) on Templates Containing 1,2-dihydro-2-oxoadenine
Abstract
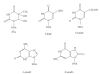
Escherichia coli DNA polymerase IV (Pol IV) is involved in bypass replication of damaged bases in DNA. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are generated continuously during normal metabolism and as a result of exogenous stress such as ionizing radiation. ROS induce various kinds of base damage in DNA. It is important to examine whether Pol IV is able to bypass oxidatively damaged bases. In this study, recombinant Pol IV was incubated with oligonucleotides containing thymine glycol (dTg), 5-formyluracil (5-fodU), 5-hydroxymethyluracil (5-hmdU), 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine (8-oxodG) and 1,2-dihydro-2-oxoadenine (2-oxodA). Primer extension assays revealed that Pol IV preferred to insert dATP opposite 5-fodU and 5-hmdU, while it inefficiently inserted nucleotides opposite dTg. Pol IV inserted dCTP and dATP opposite 8-oxodG, while the ability was low. It inserted dCTP more effectively than dTTP opposite 2-oxodA. Pol IV's ability to bypass these lesions decreased in the order: 2-oxodA > 5-fodU~5-hmdU > 8-oxodG > dTg. The fact that Pol IV preferred to insert dCTP opposite 2-oxodA suggests the mutagenic potential of 2-oxodA leading to A:T→G:C transitions. Hydrogen peroxide caused an ~2-fold increase in A:T→G:C mutations in E. coli, while the increase was significantly greater in E. coli overexpressing Pol IV. These results indicate that Pol IV may be involved in ROS-enhanced A:T→G:C mutations.
Figures

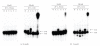

References
-
- Ohmori H, Friedberg EC, Fuchs RPP, et al. The Y-family of DNA polymerases. Molecular Cell. 2001;8(1):7–8. - PubMed
-
- Jarosz DF, Beuning PJ, Cohen SE, Walker GC. Y-family DNA polymerases in Escherichia coli . Trends in Microbiology. 2007;15(2):70–77. - PubMed
-
- Lehmann AR, Niimi A, Ogi T, et al. Translesion synthesis: Y-family polymerases and the polymerase switch. DNA Repair. 2007;6(7):891–899. - PubMed
-
- Wagner J, Gruz P, Kim S-R, et al. The dinB gene encodes a novel E. coli DNA polymerase, DNA pol IV, involved in mutagenesis. Molecular Cell. 1999;4(2):281–286. - PubMed
-
- Tang M, Pham P, Shen X, et al. Roles of E. coli DNA polymerases IV and V in lesion-targeted and untargeted SOS mutagenesis. Nature. 2000;404(6781):1014–1018. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

