IL28B polymorphism does not determine outcomes of hepatitis B virus or HIV infection
- PMID: 20977343
- PMCID: PMC2974014
- DOI: 10.1086/657146
IL28B polymorphism does not determine outcomes of hepatitis B virus or HIV infection
Abstract
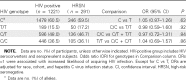
An IL28B haplotype strongly determines the outcome of natural and interferon-α treated hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. To assess whether the polymorphism marking the haplotype (rs12979860) also affects other interferon-α responsive chronic viral illnesses, namely hepatitis B virus (HBV) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 infections, we genotyped 226 individuals with HBV persistence, 384 with HBV recovery, and 2548 with or at high risk for HIV infection. The C/C genotype of rs12979860 was not associated with HBV recovery (odds ratio, 0.99), resistance to HIV infection (odds ratio, 0.97), or HIV disease progression (P > .05). This IL28B single-nucleotide polymorphism affects the immune response to HCV but not to HBV or HIV.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest: none reported.
Figures


References
-
- Marcello T, Grakoui A, Barba-Spaeth G, et al. Interferons alpha and lambda inhibit hepatitis C virus replication with distinct signal transduction and gene regulation kinetics. Gastroenterology. 2006;131(6):1887–1898. - PubMed
-
- Ge D, Fellay J, Thompson AJ, et al. Genetic variation in IL28B predicts hepatitis C treatment-induced viral clearance. Nature. 2009;461(7262):399–401. - PubMed
-
- Lapenta C, Santini SM, Proietti E, et al. Type I interferon is a powerful inhibitor of in vivo HIV-1 infection and preserves human CD4 +T cells from virus-induced depletion in SCID mice transplanted with human cells. Virology. 1999;263(1):78–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01-DA-12568/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI037984/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DA004334/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-35042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA004334/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-35040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MO1-RR00071/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HD-4-3200/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CO012400/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD041224/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR002558/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5-MO1-RR-00722/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA-04334/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K07 CA140360/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-37984/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MO1-RR02558/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- MO1-RR00059/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI037613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-35041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000071/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000059/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000722/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HD-4-1224/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- N02 CP055504/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-35039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012568/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CO-12400/CO/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MO1-RR06020/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-35043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI-37613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

