The acute antinociceptive effect of HBO₂ is mediated by a NO-cyclic GMP-PKG-KATP channel pathway in mice
- PMID: 20977894
- PMCID: PMC3023906
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.10.079
The acute antinociceptive effect of HBO₂ is mediated by a NO-cyclic GMP-PKG-KATP channel pathway in mice
Abstract
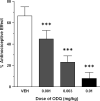
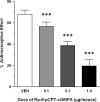
Previous research has found that hyperbaric oxygen (HBO(2)) produces an acute antinociceptive effect that is dependent on nitric oxide (NO). The present study was undertaken to determine whether HBO(2)-induced acute antinociception might involve a NO-cyclic GMP-protein kinase G-ATP-sensitive potassium (K(ATP)) channel pathway. Male NIH Swiss mice were subjected to a 5-min HBO(2) treatment (100% oxygen at 3.5 absolute atmospheres) and antinociception was assessed over the next 6 min still under HBO(2) using the acetic acid abdominal constriction test. Pretreatment with 2-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1H-imidazolyl-1-oxy-3-oxide (carboxy-PTIO, an NO scavenger), 1H-[1,2,4]-oxadiazolo-[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one) (a soluble guanylyl cyclase-inhibitor, Rp-8-(4-chlorophenylthio)-guanosine-3',5'-cyclic monophosphorothioate (a protein kinase G-inhibitor) or glibenclamide (an ATP-sensitive potassium channel-inhibitor) all led to antagonism of the HBO(2)-induced acute antinociception in a dose-dependent manner. These findings suggest that HBO(2)-induced acute antinociception might be due to activation of a NO-cyclic GMP-protein kinase G-K(ATP) channel pathway.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Akaike T, Yoshida M, Miyamoto Y, Sato K, Kohno M, Sasamoto K, Miyazaki K, Ueda S, Maeda H. Antagonistic action of imidazolineoxyl N-oxides against endothelium-derived relaxing factor/•NO through a radical reaction. Biochemistry. 1993;32:827–832. - PubMed
-
- Barnstable CJ, Wei JY, Han MH. Modulation of synaptic function by cGMP and cGMP-gated cation channels. Neurochem. Int. 2004;45:875–884. - PubMed
-
- Brito GAC, Sachs D, Cunha FQ, Vale ML, Lotufo CMC, Ferreira SH, Ribeiro RA. Peripheral antinociceptive effect of pertussis toxin: activation of the arginine/NO/cGMP/PKG/ATP-sensitive K+ channel pathway. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006;24:1175–1181. - PubMed
-
- Butt E, Eigenthaler M, Genieser HG. (Rp)-8-pCPT-cGMPS, a novel cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1994;269:265–268. - PubMed
-
- Calabrese V, Mancuso C, Calvani M, Rizzarelli E, Butterfield DA, Stella AM. Nitric oxide in the central nervous system: neuroprotection versus neurotoxicity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007;8:766–775. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

