A dual role for ErbB2 signaling in cardiac trabeculation
- PMID: 20978078
- PMCID: PMC3049280
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.053736
A dual role for ErbB2 signaling in cardiac trabeculation
Abstract
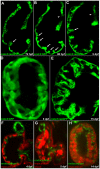
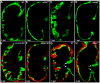
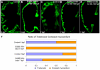
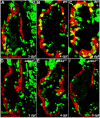
Cardiac trabeculation is a crucial morphogenetic process by which clusters of ventricular cardiomyocytes extrude and expand into the cardiac jelly to form sheet-like projections. Although it has been suggested that cardiac trabeculae enhance cardiac contractility and intra-ventricular conduction, their exact function in heart development has not been directly addressed. We found that in zebrafish erbb2 mutants, which we show completely lack cardiac trabeculae, cardiac function is significantly compromised, with mutant hearts exhibiting decreased fractional shortening and an immature conduction pattern. To begin to elucidate the cellular mechanisms of ErbB2 function in cardiac trabeculation, we analyzed erbb2 mutant hearts more closely and found that loss of ErbB2 activity resulted in a complete absence of cardiomyocyte proliferation during trabeculation stages. In addition, based on data obtained from proliferation, lineage tracing and transplantation studies, we propose that cardiac trabeculation is initiated by directional cardiomyocyte migration rather than oriented cell division, and that ErbB2 cell-autonomously regulates this process.
Figures


References
-
- Bartman T., Hove J. (2005). Mechanics and function in heart morphogenesis. Dev. Dyn. 233, 373-381 - PubMed
-
- Ben-Shachar G., Arcilla R. A., Lucas R. V., Manasek F. J. (1985). Ventricular trabeculations in the chick embryo heart and their contribution to ventricular and muscular septal development. Circ. Res. 57, 759-766 - PubMed
-
- Bersell K., Arab S., Haring B., Kuhn B. (2009). Neuregulin1/ErbB4 signaling induces cardiomyocyte proliferation and repair of heart injury. Cell 138, 257-270 - PubMed
-
- Busse D., Doughty R. S., Ramsey T. T., Russell W. E., Price J. O., Flanagan W. M., Shawver L. K., Arteaga C. L. (2000). Reversible G(1) arrest induced by inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase requires up-regulation of p27(KIP1) independent of MAPK activity. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 6987-6995 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

