Thiocolchicoside exhibits anticancer effects through downregulation of NF-κB pathway and its regulated gene products linked to inflammation and cancer
- PMID: 20978115
- PMCID: PMC3142676
- DOI: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0037
Thiocolchicoside exhibits anticancer effects through downregulation of NF-κB pathway and its regulated gene products linked to inflammation and cancer
Abstract
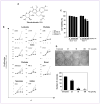
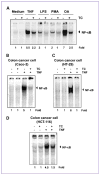
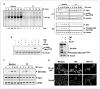
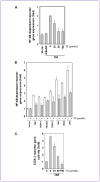
The discovery of new uses for older, clinically approved drugs is one way to expedite drug development for cancer. Thiocolchicoside, a semisynthetic colchicoside from the plant Gloriosa superba, is a muscle relaxant and used to treat rheumatologic and orthopedic disorders because of its analgesic and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Given that activation of the transcription factor NF-κB plays a major role in inflammation and tumorigenesis, we postulated that thiocolchicoside would inhibit NF-κB and exhibit anticancer effects through the modulation of NF-κB-regulated proteins. We show that thiocolchicoside inhibited proliferation of leukemia, myeloma, squamous cell carcinoma, breast, colon, and kidney cancer cells. Formation of tumor colonies was also suppressed by thiocolchicoside. The colchicoside induced apoptosis, as indicated by caspase-3 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage, and suppressed the expression of cell survival [e.g., Bcl-2, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP), MCL-1, bcl-xL, cIAP-1, cIAP-2, and cFLIP] proteins. Cell proliferation biomarkers such as c-MYC and phosphorylation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase and glycogen synthase kinase 3β were also blocked by thiocolchicoside. Because most cell survival and proliferation gene products are regulated by NF-κB, we studied the effect of thiocolchicoside on this transcription factor and found that thiocolchicoside inhibited NF-κB activation, degradation of inhibitory κBα (IκBα), IκBα ubiquitination, and phosphorylation, abolished the activation of IκBα kinase, and suppressed p65 nuclear translocation. This effect of thiocolchicoside on the NF-κB pathway led to inhibition of NF-κB reporter activity and cyclooxygenase-2 promoter activity. Our results indicate that thiocolchicoside exhibits anticancer activity through inhibition of NF-κB and NF-κB-regulated gene products, which provides novel insight into a half-century old drug.
©2010 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures


References
-
- Janbroers JM. Review of the toxicology, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of thiocolchicoside, a GABA-agonist muscle relaxant with anti-inflammatory and analgesic actions. Acta Therapeutica. 1987;13:221–35.
-
- Tuzun F, Unalan H, Oner N, et al. Multicenter, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial of thiocolchicoside in acute low back pain. Joint Bone Spine. 2003;70:356–61. - PubMed
-
- Ketenci A, Ozcan E, Karamursel S. Assessment of efficacy and psychomotor performances of thiocolchicoside and tizanidine in patients with acute low back pain. Int J Clin Pract. 2005;59:764–70. - PubMed
-
- Soonawalla DF, Joshi N. Efficacy of thiocolchicoside in Indian patients suffering from low back pain associated with muscle spasm. J Indian Med Assoc. 2008;106:331–5. - PubMed
-
- Balduini W, Cimino M, Depoortere H, Cattabeni F. Characterization of [3H]thiocolchicoside binding sites in rat spinal cord and cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999;376:149–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

