Epithelial Notch signaling regulates interstitial fibrosis development in the kidneys of mice and humans
- PMID: 20978353
- PMCID: PMC2964979
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI43025
Epithelial Notch signaling regulates interstitial fibrosis development in the kidneys of mice and humans
Abstract
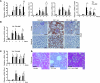
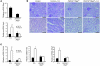
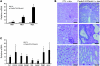
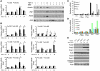
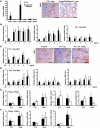
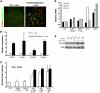
Chronic kidney disease is a leading cause of death in the United States. Tubulointerstitial fibrosis (TIF) is considered the final common pathway leading to end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Here, we used pharmacologic, genetic, in vivo, and in vitro experiments to show that activation of the Notch pathway in tubular epithelial cells (TECs) in patients and in mouse models of TIF plays a role in TIF development. Expression of Notch in renal TECs was found to be both necessary and sufficient for TIF development. Genetic deletion of the Notch pathway in TECs reduced renal fibrosis. Consistent with this, TEC-specific expression of active Notch1 caused rapid development of TIF. Pharmacologic inhibition of Notch activation using a γ-secretase inhibitor ameliorated TIF. In summary, our experiments establish that epithelial injury and Notch signaling play key roles in fibrosis development and indicate that Notch blockade may be a therapeutic strategy to reduce fibrosis and ESRD development.
Figures

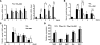


References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). State-specific trends in chronic kidney failure--United States, 1990–2001. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2004;53(39):918–920. - PubMed
-
- Nath KA. Tubulointerstitial changes as a major determinant in the progression of renal damage. Am J Kidney Dis. 1992;20(1):1–17. - PubMed
-
- Kriz W, et al. How does podocyte damage result in tubular damage? Kidney Blood Press Res. 1999;22(1–2):26–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

