Inhibition of renin-angiotensin system affects prognosis of advanced pancreatic cancer receiving gemcitabine
- PMID: 20978506
- PMCID: PMC2994224
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605955
Inhibition of renin-angiotensin system affects prognosis of advanced pancreatic cancer receiving gemcitabine
Abstract
Background: The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is thought to have a role in carcinogenesis, and RAS inhibition may prevent tumour growth.
Methods: We retrospectively investigated the impact of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and angiotensin II type-1 receptor blockers (ARBs) in 155 patients with pancreatic cancer receiving gemcitabine monotherapy. Patients were divided into three groups: the ACEI/ARB group (27 patients receiving an ACEI or ARB for hypertension (HT)), the non-ACEI/ARB with HT group (25 patients receiving antihypertensive drugs other than ACEIs or ARBs), and the non-HT group (103 patients receiving no antihypertensive drugs).
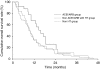
Results: Patient characteristics were not different, except for age and HT medications. Progression-free survival (PFS) was 8.7 months in the ACEI/ARB group, 4.5 months in the non-ACEI/ARB with HT group, and 3.6 months in the non-HT group. Overall survival (OS) was 15.1 months in the ACEI/ARB group, 8.9 months in the non-ACEI/ARB with HT group, and 9.5 months in the non-HT group. The use of ACEIs/ARBs was a significant prognostic factor for both PFS (P=0.032) and OS (P=0.014) in the multivariate analysis.
Conclusions: The ACEIs/ARBs in combination with gemcitabine might improve clinical outcomes in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Prospective trials are needed to test this hypothesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ager EI, Neo J, Christophi C (2008) The renin-angiotensin system and malignancy. Carcinogenesis 29(9): 1675–1684 - PubMed
-
- Amaya K, Ohta T, Kitagawa H, Kayahara M, Takamura H, Fujimura T, Nishimura G, Shimizu K, Miwa K (2004) Angiotensin II activates MAP kinase and NF-kappaB through angiotensin II type I receptor in human pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol 25(4): 849–856 - PubMed
-
- Arafat HA, Gong Q, Chipitsyna G, , Rizvi A, , Saa CT, Yeo CJ (2007) Antihypertensives as novel antineoplastics: angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Am Coll Surg 204(5): 996–1005; discussion 1005–1006 - PubMed
-
- Berlin JD, Catalano P, Thomas JP, Kugler JW, Haller DG, Benson III AB (2002) Phase III study of gemcitabine in combination with fluorouracil versus gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic carcinoma: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Trial E2297. J Clin Oncol 20(15): 3270–3275 - PubMed
-
- Burris III H, Rocha-Lima C (2008) New therapeutic directions for advanced pancreatic cancer: targeting the epidermal growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor pathways. Oncologist 13(3): 289–298 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

