Valproic acid attenuates blood-brain barrier disruption in a rat model of transient focal cerebral ischemia: the roles of HDAC and MMP-9 inhibition
- PMID: 20978517
- PMCID: PMC3049473
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.195
Valproic acid attenuates blood-brain barrier disruption in a rat model of transient focal cerebral ischemia: the roles of HDAC and MMP-9 inhibition
Abstract
Valproic acid (VPA), a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, is known to protect against cerebral ischemia. The effects of VPA on blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption were investigated in rats subjected to transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). Postischemic VPA treatment remarkably attenuated MCAO-induced BBB disruption and brain edema. Meanwhile, VPA significantly reduced MCAO-induced elevation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), degradation of tight junction proteins, and nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). Sodium butyrate, another HDAC inhibitor, mimicked these effects of VPA. Our findings suggest that BBB protection by VPA involves HDAC inhibition-mediated suppression of NF-κB activation, MMP-9 induction, and tight junction degradation.
Figures

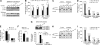
References
-
- Cheng T, Petraglia AL, Li Z, Thiyagarajan M, Zhong Z, Wu Z, Liu D, Maggirwar SB, Deane R, Fernandez JA, LaRue B, Griffin JH, Chopp M, Zlokovic BV. Activated protein C inhibits tissue plasminogen activator-induced brain hemorrhage. Nat Med. 2006;12:1278–1285. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham LA, Wetzel M, Rosenberg GA. Multiple roles for MMPs and TIMPs in cerebral ischemia. Glia. 2005;50:329–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

