Intratympanic steroids in severe to profound sudden sensorineural hearing loss as salvage treatment
- PMID: 20978628
- PMCID: PMC2958501
- DOI: 10.3342/ceo.2010.3.3.122
Intratympanic steroids in severe to profound sudden sensorineural hearing loss as salvage treatment
Abstract
Objectives: Intratympanic steroids are being increasingly used in the treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) after the failure of systemic therapy. This study evaluated the efficacy of administering intratympanic dexamethasone (ITD) as a salvage treatment for severe to profound SSNHL.
Methods: We reviewed the medical records of patients who presented with severe to profound SSNHL between January 2007 and December 2009. ITD was given about 14 days after the initial systemic treatment. Successful recovery was defined as complete or partial recovery using Sigel's criteria. We compared the results of treatment between the severe SSNHL (S-SSNHL) and profound SSNHL (P-SSNHL) groups.
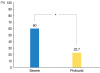
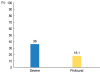
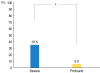
Results: All the patients in the S-SSNHL group showed significant improvement, as compared to the P-SSNHL group (P=0.017). The recovery rate after the initial systemic treatment was 36% (9/25) in the S-SSNHL group and 18.1% (4/22) in the P-SSNHL group (P=0.207). In comparison, the recovery rate of ITD as a salvage treatment was 37.5% (6/16) in the S-SSNHL group and 5.5% (1/18) in the P-SSNHL group (P=0.03).
Conclusion: Our comparative study dose not support the efficacy of ITD as salvage treatment for patients with P-SSNHL as compared with that for S-SSNHL. We recommend that patients with P-SSNHL be informed about the low efficacy of ITD as a salvage treatment.
Keywords: Intratympanic; Steroid; Sudden sensorineural hearing loss.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Wilson WR, Byl FM, Laird N. The efficacy of steroids in the treatment of idiopathic sudden hearing loss: a double-blind clinical study. Arch Otolaryngol. 1980 Dec;106(12):772–776. - PubMed
-
- Byl FM., Jr Sudden hearing loss: eight years' experience and suggested prognostic table. Laryngoscope. 1984 May;94(5 Pt 1):647–661. - PubMed
-
- Mattox DE, Lyles CA. Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Am J Otol. 1989 May;10(3):242–247. - PubMed
-
- Moskowitz D, Lee KJ, Smith HW. Steroid use in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope. 1984 May;94(5 Pt 1):664–666. - PubMed
-
- Parnes LS, Sun AH, Freeman DJ. Corticosteroid pharmacokinetics in the inner ear fluids: an animal study followed by clinical application. Laryngoscope. 1999 Jul;109(7 Pt 2):1–17. - PubMed

