miR-194 is a marker of hepatic epithelial cells and suppresses metastasis of liver cancer cells in mice
- PMID: 20979124
- PMCID: PMC3076553
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.23915
miR-194 is a marker of hepatic epithelial cells and suppresses metastasis of liver cancer cells in mice
Abstract
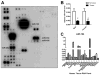
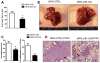
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression by interacting with the 3' untranslated region (3'-UTR) of multiple mRNAs. Recent studies have linked miRNAs to the development of cancer metastasis. In this study, we show that miR-194 is specifically expressed in the human gastrointestinal tract and kidney. Moreover, miR-194 is highly expressed in hepatic epithelial cells, but not in Kupffer cells or hepatic stellate cells, two types of mesenchymal cells in the liver. miR-194 expression was decreased in hepatocytes cultured in vitro, which had undergone a dedifferentiation process. Furthermore, expression of miR-194 was low in liver mesenchymal-like cancer cell lines. The overexpression of miR-194 in liver mesenchymal-like cancer cells reduced the expression of the mesenchymal cell marker N-cadherin and suppressed invasion and migration of the mesenchymal-like cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. We further demonstrated that miR-194 targeted the 3'-UTRs of several genes that were involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer metastasis.
Conclusion: These results support a role of miR-194, which is specifically expressed in liver parenchymal cells, in preventing liver cancer cell metastasis.
Copyright © 2010 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: Nothing to report.
Figures
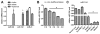
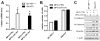

References
-
- Taub R. Liver regeneration: from myth to mechanism. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:836–847. - PubMed
-
- Huber MA, Kraut N, Beug H. Molecular requirements for epithelial-mesenchymal transition during tumor progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17:548–558. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, et al. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:593–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
