Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 20979469
- PMCID: PMC3014291
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1006448
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer
Erratum in
- N Engl J Med. 2011 Feb 10;364(6):588
Abstract
Background: Oncogenic fusion genes consisting of EML4 and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) are present in a subgroup of non-small-cell lung cancers, representing 2 to 7% of such tumors. We explored the therapeutic efficacy of inhibiting ALK in such tumors in an early-phase clinical trial of crizotinib (PF-02341066), an orally available small-molecule inhibitor of the ALK tyrosine kinase.
Methods: After screening tumor samples from approximately 1500 patients with non-small-cell lung cancer for the presence of ALK rearrangements, we identified 82 patients with advanced ALK-positive disease who were eligible for the clinical trial. Most of the patients had received previous treatment. These patients were enrolled in an expanded cohort study instituted after phase 1 dose escalation had established a recommended crizotinib dose of 250 mg twice daily in 28-day cycles. Patients were assessed for adverse events and response to therapy.
Results: Patients with ALK rearrangements tended to be younger than those without the rearrangements, and most of the patients had little or no exposure to tobacco and had adenocarcinomas. At a mean treatment duration of 6.4 months, the overall response rate was 57% (47 of 82 patients, with 46 confirmed partial responses and 1 confirmed complete response); 27 patients (33%) had stable disease. A total of 63 of 82 patients (77%) were continuing to receive crizotinib at the time of data cutoff, and the estimated probability of 6-month progression-free survival was 72%, with no median for the study reached. The drug resulted in grade 1 or 2 (mild) gastrointestinal side effects.
Conclusions: The inhibition of ALK in lung tumors with the ALK rearrangement resulted in tumor shrinkage or stable disease in most patients. (Funded by Pfizer and others; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT00585195.).
Figures

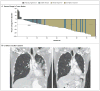
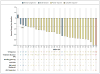

Comment in
-
Crizotinib--latest champion in the cancer wars?N Engl J Med. 2010 Oct 28;363(18):1760-2. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1010404. N Engl J Med. 2010. PMID: 20979477 No abstract available.
-
ALK and resistance.Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 Dec;10(12):817. doi: 10.1038/nrc2976. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21155181 No abstract available.
-
Crizotinib for EML4-ALK positive lung adenocarcinoma: a hope for the advanced disease? Evaluation of Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2010;363(18):1693-703.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011 Mar;15(3):351-3. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2011.550880. Epub 2011 Jan 5. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011. PMID: 21208134
-
More on crizotinib.N Engl J Med. 2011 Feb 24;364(8):776-7; author reply 778. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1013325. N Engl J Med. 2011. PMID: 21345113 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non–small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–39. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–500. - PubMed
-
- Kutok JL, Aster JC. Molecular biology of anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:3691–702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- P20 CA090578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA058187/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58187/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA090578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA136851/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA090578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA47179/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA047179/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46934/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046934/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA062203/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA06516/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA006516/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA136851/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
