β-cell dysfunctional ERAD/ubiquitin/proteasome system in type 2 diabetes mediated by islet amyloid polypeptide-induced UCH-L1 deficiency
- PMID: 20980462
- PMCID: PMC3012175
- DOI: 10.2337/db10-0522
β-cell dysfunctional ERAD/ubiquitin/proteasome system in type 2 diabetes mediated by islet amyloid polypeptide-induced UCH-L1 deficiency
Erratum in
-
Erratum. β-Cell Dysfunctional ERAD/Ubiquitin/Proteasome System in Type 2 Diabetes Mediated by Islet Amyloid Polypeptide-Induced UCH-L1 Deficiency. Diabetes 2011;60:227-238.Diabetes. 2023 Dec 1;72(12):1881. doi: 10.2337/db23-er12. Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 37683136 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: The islet in type 2 diabetes is characterized by β-cell apoptosis, β-cell endoplasmic reticulum stress, and islet amyloid deposits derived from islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP). Toxic oligomers of IAPP form intracellularly in β-cells in humans with type 2 diabetes, suggesting impaired clearance of misfolded proteins. In this study, we investigated whether human-IAPP (h-IAPP) disrupts the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation/ubiquitin/proteasome system.
Research design and methods: We used pancreatic tissue from humans with and without type 2 diabetes, isolated islets from h-IAPP transgenic rats, isolated human islets, and INS 832/13 cells transduced with adenoviruses expressing either h-IAPP or a comparable expression of rodent-IAPP. Immunofluorescence and Western blotting were used to detect polyubiquitinated proteins and ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1) protein levels. Proteasome activity was measured in isolated rat and human islets. UCH-L1 was knocked down by small-interfering RNA in INS 832/13 cells and apoptosis was evaluated.
Results: We report accumulation of polyubiquinated proteins and UCH-L1 deficiency in β-cells of humans with type 2 diabetes. These findings were reproduced by expression of oligomeric h-IAPP but not soluble rat-IAPP. Downregulation of UCH-L1 expression and activity to reproduce that caused by h-IAPP in β-cells induced endoplasmic reticulum stress leading to apoptosis.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that defective protein degradation in β-cells in type 2 diabetes can, at least in part, be attributed to misfolded h-IAPP leading to UCH-L1 deficiency, which in turn further compromises β-cell viability.
Figures




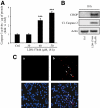
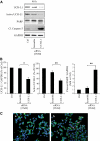

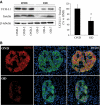
Similar articles
-
UCHL1 deficiency exacerbates human islet amyloid polypeptide toxicity in β-cells: evidence of interplay between the ubiquitin/proteasome system and autophagy.Autophagy. 2014 Jun;10(6):1004-14. doi: 10.4161/auto.28478. Autophagy. 2014. PMID: 24879150 Free PMC article.
-
Functional proteasome complex is required for turnover of islet amyloid polypeptide in pancreatic β-cells.J Biol Chem. 2018 Sep 14;293(37):14210-14223. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002414. Epub 2018 Jul 16. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30012886 Free PMC article.
-
Successful versus failed adaptation to high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance: the role of IAPP-induced beta-cell endoplasmic reticulum stress.Diabetes. 2009 Apr;58(4):906-16. doi: 10.2337/db08-1464. Epub 2009 Jan 16. Diabetes. 2009. PMID: 19151199 Free PMC article.
-
Islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) transgenic rodents as models for type 2 diabetes.ILAR J. 2006;47(3):225-33. doi: 10.1093/ilar.47.3.225. ILAR J. 2006. PMID: 16804197 Review.
-
The β-cell assassin: IAPP cytotoxicity.J Mol Endocrinol. 2017 Oct;59(3):R121-R140. doi: 10.1530/JME-17-0105. Epub 2017 Aug 15. J Mol Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28811318 Review.
Cited by
-
Impaired proteostasis: role in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus.Diabetologia. 2014 Aug;57(8):1517-27. doi: 10.1007/s00125-014-3257-1. Epub 2014 May 11. Diabetologia. 2014. PMID: 24816368 Review.
-
Genome-wide association study identifies African-ancestry specific variants for metabolic syndrome.Mol Genet Metab. 2015 Dec;116(4):305-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2015.10.008. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Mol Genet Metab. 2015. PMID: 26507551 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of Fas protects islet beta cells from cytotoxic effects of human islet amyloid polypeptide.Diabetologia. 2012 Feb 1. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2451-2. Online ahead of print. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22301943
-
A new target for an old DUB: UCH-L1 regulates mitofusin-2 levels, altering mitochondrial morphology, function and calcium uptake.Redox Biol. 2020 Oct;37:101676. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101676. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 32956978 Free PMC article.
-
β Cell-specific increased expression of calpastatin prevents diabetes induced by islet amyloid polypeptide toxicity.JCI Insight. 2016 Nov 3;1(18):e89590. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.89590. JCI Insight. 2016. PMID: 27812546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang CJ, Lin CY, Haataja L, Gurlo T, Butler AE, Rizza RA, Butler PC: High expression rates of human islet amyloid polypeptide induce endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated β-cell apoptosis, a characteristic of humans with type 2 but not type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2007;56:2016–2027 - PubMed
-
- Marchetti P, Bugliani M, Lupi R, Marselli L, Masini M, Boggi U, Filipponi F, Weir GC, Eizirik DL, Cnop M: The endoplasmic reticulum in pancreatic beta cells of type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetologia 2007;50:2486–2494 - PubMed
-
- Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, Butler PC: β-Cell deficit and increased β-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003;52:102–110 - PubMed
-
- Laybutt DR, Preston AM, Akerfeldt MC, Kench JG, Busch AK, Biankin AV, Biden TJ: Endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to beta cell apoptosis in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2007;50:752–763 - PubMed
-
- Kloppel G, Lohr M, Habich K, Oberholzer M, Heitz PU: Islet pathology and the pathogenesis of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus revisited. Surv Synth Pathol Res 1985;4:110–125 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

