Lung cancer risk and genetic polymorphisms in DNA repair pathways: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 20981350
- PMCID: PMC2958337
- DOI: 10.4061/2010/701760
Lung cancer risk and genetic polymorphisms in DNA repair pathways: a meta-analysis
Abstract
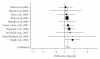
Genetic variations in DNA repair genes are thought to modulate DNA repair capacity and are suggested to be related to lung cancer risk. We conducted a meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies on the association between genetic polymorphisms in both base excision repair and nucleotide excision repair pathways, and lung cancer. We found xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group A (XPA) G23A (odds ratio (OR) = 0.76, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.61-0.94), 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 (OGG1) Ser326Cys (OR = 1.22, 95% CI = 1.02-1.45), and excision repair cross-complementing group 2 (ERCC2) Lys751Gln (OR = 1.27, 95% CI = 1.10-1.46) polymorphisms were associated with lung cancer risk. Considering the data available, it can be conjectured that if there is any risk association between a single SNP and lung cancer, the risk fluctuation will probably be minimal. Advances in the identification of new polymorphisms and in high-throughput genotyping techniques will facilitate the analysis of multiple genes in multiple DNA repair pathways. Therefore, it is likely that the defining feature of future epidemiologic studies will be the simultaneous analysis of large samples of cases and controls.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetic polymorphisms in the nucleotide excision repair pathway and lung cancer risk: a meta-analysis.Int J Med Sci. 2007 Feb 1;4(2):59-71. doi: 10.7150/ijms.4.59. Int J Med Sci. 2007. PMID: 17299578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of genetic polymorphisms in the base excision repair pathway with lung cancer risk: a meta-analysis.Lung Cancer. 2006 Dec;54(3):267-83. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2006.08.009. Epub 2006 Sep 18. Lung Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16982113 Review.
-
Association of genetic polymorphisms in DNA repair pathway genes with non-small cell lung cancer risk.Lung Cancer. 2011 Aug;73(2):138-46. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2010.11.018. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Lung Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21195504
-
Polymorphisms in base-excision repair and nucleotide-excision repair genes in relation to lung cancer risk.Mutat Res. 2007 Jul 28;631(2):101-10. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2007.03.010. Epub 2007 Apr 21. Mutat Res. 2007. PMID: 17531525
-
Pterygium and genetic polymorphisms of the DNA repair enzymes XRCC1, XPA, and XPD.Mol Vis. 2010 Apr 20;16:698-704. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 20431719 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The hOGG1Ser326Cys polymorphism and increased lung cancer susceptibility in Caucasians: an updated meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2012;2:548. doi: 10.1038/srep00548. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Sci Rep. 2012. PMID: 22855704 Free PMC article.
-
XPA: DNA Repair Protein of Significant Clinical Importance.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 22;21(6):2182. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062182. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32235701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment and characterization of a lung cancer cell line, SMC-L001, from a lung adenocarcinoma.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2014 Jun;50(6):519-26. doi: 10.1007/s11626-014-9736-3. Epub 2014 Feb 26. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2014. PMID: 24569940
-
Haplotype analysis of XRCC2 gene polymorphisms and association with increased risk of head and neck cancer.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 16;7(1):13210. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13461-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29038438 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the ERCC5 Asp1104His polymorphism and cancer risk: a meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e36293. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036293. Epub 2012 Jul 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22815677 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pharoah PDP, Dunning AM, Ponder BAJ, Easton DF. Association studies for finding cancer-susceptibility genetic variants. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2004;4(11):850–860. - PubMed
-
- Hecht SS. Tobacco smoke carcinogens and lung cancer. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 1999;91(14):1194–1210. - PubMed
-
- Livneh Z. DNA damage control by novel DNA polymerases: translesion replication and mutagenesis. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2001;276(28):25639–25642. - PubMed
-
- Berwick M, Vineis P. Markers of DNA repair and susceptibility to cancer in humans: an epidemiologic review. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 2000;92(11):874–897. - PubMed
-
- Wei Q, Cheng L, Amos CI, et al. Repair of tobacco carcinogen-induced DNA adducts and lung cancer risk: a molecular epidemiologic study. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 2000;92(21):1764–1772. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

